NADI reagent
The NADI reagent is an aqueous solution of 1- Na phthol and N , N - di methyl-1,4-phenylenediamine , which for the detection of the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase ( oxidase test ) in bacteria and in the histology is used. Phenylenediamine reduces cytochrome c oxidase in the cell via cytochrome c and is thereby oxidized to quinonediimine. Quinonediimine couples with the naphthol to form a colorless leuco compound , which is oxidized to the dye indophenol blue . In 1885 Paul Ehrlich described the NADI reaction with the formation of indophenol in the organism as a reaction of an indophenol oxidase .
Reagent
The NADI reagent consists of a solution in equal parts of 50 mM 1-naphthol in 50% ethanol and 50 mM N , N- dimethyl- p- phenylenediamine in a phosphate buffer (pH 7).
If the bacterium cells turn blue within one minute of adding the reagent, the bacterium is oxidase-positive. If there is no or later reaction, the bacterium is oxidase-negative.
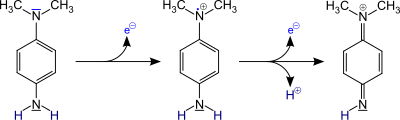
Reaction mechanism
The p -phenylenediamine derivative is oxidized to the quinonediimine derivative via the colored, stable semiquinonediimine radical cation (Wurster red):
The quinonediimine derivative reacts with the coupler (naphthol) to form a colorless leuco compound. Oxidation of the leuco compound creates the water-insoluble quinone imine dye indophenol blue:
Individual evidence
- ↑ WL Gaby, C. Hadley: Practical laboratory test for the identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa , in: J. Bacteriol. 1957, 74 , 356-358, PMID 13475249 , PMC 314647 (free full text).
- ↑ P. Ehrlich: The organism's need for oxygen. A color analytical study . Habilitation thesis, University of Berlin 1885 .
- ↑ U. Nickel: Reactions with Wurster's cations , in: Chemistry in our time 1978, 12 , 89-98; doi : 10.1002 / ciuz.19780120305 .