Narcinidae
| Narcinidae | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

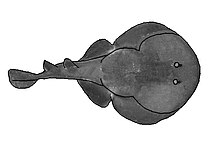
Eye spot electric ray ( Diplobatis ommata ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Narcinidae | ||||||||||||
| Gill , 1862 |
The rays of the family narcinidae ( Gr . "Narke" = paralysis) are close relatives of the electric ray (Torpedinidae). The almost 30 species are rather small animals 18 to 76 centimeters in length. Most species remain below half a meter in length.
features
They are disc-shaped, sometimes elongated, have a shark-like tail with a caudal fin and 0 to 2 dorsal fins. The body is bare and not covered with thorns or placoid scales on either the top or the bottom . The head is broad and flattened, the rostrum ends rounded or blunt, with rounded corners. The eyes on the top of the head are just before the injection holes or almost in between. The mouth has no labial folds but clear pits at the corners of the mouth. The nostrils are located just in front of the mouth at a distance that is much smaller than the diameter of the nostrils. They are connected by wide nasal pits. The anterior nasal valves are short, flared at the sides and fused together. They slightly overlap the mouth. On the underside there are five small gill openings on each side just before the center of the base of the pectoral fin. Gill trap rays are absent. The mouth has no labial folds but clear pits at the corners of the mouth. The nostrils are located just in front of the mouth at a distance that is much smaller than the diameter of the nostrils. They are connected by wide nasal pits. The anterior nasal valves are short, flared at the sides and fused together. They slightly overlap the mouth. The tail can be the same length or longer than the body disc. The tail is only slightly flattened laterally and usually has lateral keels. A tail spine is missing. The caudal fin is about the size of the pelvic fins and can be symmetrical or asymmetrical.
Like the real electric rays ( torpedo ), they have two kidney-shaped electrical organs on the head and front body, which consist of converted muscles and with the help of which they can paralyze prey fish through electrical discharges.
The upper side of the Narcinidae is whitish, yellowish, gray-green or brown in color. More or less pronounced spots can be present or absent. The underside is whitish, that of the deep-sea forms black.
distribution
The Narcinidae live in the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific, mostly in shallower areas, on sandy coastlines, estuaries and on the upper areas of the shelf . Benthobatis moresbyi lives at depths of 780 to 1070 meters.
Way of life
They are slow-swimming bottom dwellers that are often found on soft mud or sandy areas. As far as is known, all species are ovoviviparous . They feed on invertebrates and small fish that they ingest from the bottom. The highly protractile (protruding) mouth of the fish can be shaped into a tube and the prey sucked out of the ground. Human-captured Narcinidae can deliver a moderate electric shock if their body disc is touched.
Systematics
There are five genera and about 30 species:
- Genus Benthobatis
- Benthobatis kreffti Rincon, Stehmann & Vooren, 2001 .
- Benthobatis marcida Bean & Weed, 1909 .
- Benthobatis moresbyi Alcock , 1898 .
- Benthobatis yangi Carvalho, Compagno & Ebert, 2003 .
- Genus Diplobatis
- Diplobatis colombiensis Fechhelm & McEachran, 1984 .
- Diplobatis guamachensis Martín Salazar, 1957 .
- Eye spot electric ray ( Diplobatis ommata ) (Jordan & Gilbert, 1890) .
- Diplobatis pictus Palmer, 1950 .
- Genus Discopyge
- Discopyge castelloi Menni, Rincón & García, 2008 .
- Discopyge tschudii Heckel, 1846 .
- Genus Narcine
- Narcine atzi Carvalho & Randall, 2003 .
- Narcine baliensis Carvalho & White, 2016 .
- Narcine bancroftii (Griffith & Smith, 1834) .
- Narcine brasiliensis (Olfers, 1831) .
- Narcine brevilabiata Bessednov, 1966 .
- Narcine brunnea Annandale, 1909 .
- Narcine entemedor Jordan & Starks, 1895 .
- Narcine indica Henle , 1834 .
- Narcine insolita Carvalho, Séret & Compagno, 2002 .
- Narcine leoparda Carvalho, 2001 .
- Narcine lingula Richardson , 1846 .
- Narcine maculata (Shaw, 1804) .
- Narcine oculifera Carvalho, Compagno & Mee, 2002 .
- Narcine prodorsalis Bessednov, 1966 .
- Narcine rierai (Lloris & Rucabado, 1991) .
- Narcine timlei ( Bloch & Schneider , 1801) .
- Narcine vermiculatus Breder, 1928 .
- Genus Narcinops Whitley, 1940 .
- Narcinops lasti (Carvalho & Séret, 2002) .
- Narcinops nelsoni (Carvalho 2008) .
- Narcinops ornata (Carvalho 2008) .
- Narcinops tasmaniensis (Richardson, 1841) .
- Narcinops westraliensis (McKay, 1966) .
literature
- Joseph S. Nelson : Fishes of the World , John Wiley & Sons, 2006, ISBN 0-471-25031-7
- Compagno, LJV & PR LAST (1999): Order Torpediniformes. Narcinidae. Numbfishes . In Carpenter, KE & VH Niem (eds): FAO species identification guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific . Rome, FAO, 3: 1433-1434. PDF
Web links
- Narcinidae on Fishbase.org (English)