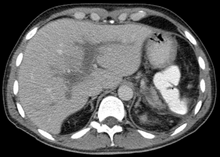
Portal vein thrombosis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| I81 | Portal vein thrombosis |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The portal vein thrombosis is a vascular disease wherein a blood clot ( thrombus ) in the portal vein has formed the liver. The portal vein (Vena portae) collects the blood from the unpaired abdominal organs (stomach, small intestine, large intestine, parts of the rectum, pancreas, spleen) and delivers it to the liver. If only individual tributaries of the portal vein are affected, one speaks of a mesenteric vein thrombosis or a splenic vein thrombosis , depending on the location . Portal vein thrombosis was first described by Balfour and Stewart in 1868 .
Symptoms
Depending on the location and size of the portal vein thrombosis, it can run completely unnoticed or it can cause symptoms due to signs of congestion in the organ areas with impaired drainage. Portal vein thrombosis can lead to esophageal varices, hemorrhoid-like rectal varices, enlargement of the spleen, and ascites. It can also have a significant impact on liver function as the blood flow to the liver is greatly reduced.
causes
A portal vein thrombosis very rarely develops spontaneously without an apparent cause. The thrombosis is usually caused by another disease. Severe pancreatitis or a pancreatic tumor can lead to obstruction and thrombosis of the portal vein or splenic vein. Liver tumors and other liver diseases can also be the cause.
Any increased tendency to clot blood (thrombophilia) can also lead to portal vein thrombosis. Causes of a coagulation disorder (hypercoagulability) can be:
- hereditary or drug-induced increased blood clotting , e.g. B. APC resistance
- a hereditary or drug-induced reduced ability to dissolve blood clots (see fibrinolysis )
- certain foods or toxins that affect blood clotting
- pregnancy
- Dehydration (increased blood viscosity)
- bacterial thrombosis in newborns with umbilical cord infection .
- (especially) in the early phase after a spleen removal (see splenectomy )
diagnosis
The diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis is made by ultrasound , computed tomography with contrast media, or magnetic resonance imaging . Since the fresh thrombosis differs only slightly from the perfused portal vein sonographically, it can easily be overlooked on ultrasound. Often only the color Doppler examination can clarify the situation. Fibrin breakdown products as a breakdown product of thrombi can be detected in the blood with a D-dimer test.
therapy
The portal vein thrombosis is treated like any other thrombosis with anticoagulant drugs such as heparin or Marcumar ( anticoagulation ). However, there is no risk of pulmonary embolism. Esophageal varices as a consequence of chronic portal vein thrombosis can be treated endoscopically (usually with rubber band ligation ). In addition, the triggering pre-existing illness is treated. This is often more important for the patient's prognosis than the thrombosis itself.
Web links
- Inflammatory, infectious and malignant diseases - risk of thrombosis in gastroenterological diseases. In: Emergency Medicine. 29, 2003, p. 200, doi : 10.1055 / s-2003-39619 .
swell
- GW Balfour, Stewart TG: Case of enlarged spleen complicated with ascites. Both depending upon varicose dilatation and thrombosis of the portal vein. In: Edinburgh Med J. 1869; 14, pp. 589-598.