Phytoene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
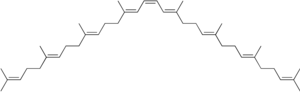
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Phytoene | |||||||||
| other names |
cis phytoene |
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 40 H 64 | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 544.9 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Phytoene is a colorless tetraterpene with 40 carbon atoms. It is an intermediate in the biological synthesis of carotenoids in plants.
Two molecules of geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) are at the start of carotene biosynthesis . The availability of GGPP limits all subsequent steps in the formation of carotene in the plant. The two GGPP molecules are linked by the enzyme phytoene synthase (PSY) to form a phytoene molecule. Phytoene synthase is a chloroplast enzyme .
The plant enzymes phytoene desaturase (PDS), ζ-Karotindesaturase (ZDS) and carotene-cis-trans isomerase (crtISO) form the red all-trans from phytoene lycopene . all-trans-lycopene is converted to β-carotene by a β-lycopene cyclase (β-LCY).
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Albert Gossauer (2003) Structure and reactivity of the biomolecules: An introduction to organic chemistry. Helvetica Chimica Acta, p. 123.
- ^ A b Gerhard Richter: Metabolic Physiology of Plants: Physiology and Biochemistry of Primary and Secondary Metabolism , Georg Thieme Verlag 1988, p. 356.