Polyphenol oxidase
| Sweet potato phenolase ( Ipomoea batatas ) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mass / length primary structure | 496 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer | |
| Cofactor | 2 copper | |
| Identifier | ||
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 1.10.3.1 , oxidoreductase | |
| Response type | oxidation | |
| Substrate | 2 mono / diphenol + O 2 | |
| Products | 2 o-dichinone + 2 H 2 O | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | plants | |
Phenolase , more precisely chloroplastic polyphenol oxidase (PPO) , formerly: catechol oxidase , is the homologue of tyrosinase in plants. In addition to the reactions of tyrosinase, it is able to oxidize phenols and catechols . These reactions are responsible for the browning of plant material after injury and contact with atmospheric oxygen. The resulting quinones are toxic to pathogenic microorganisms.
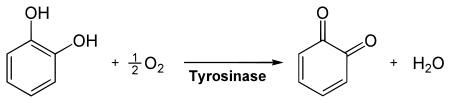
Enzymatic catalysis
During the oxidation of catechol in the presence of phenolase as a catalyst, the dihydroxybenzene is converted into benzoquinone :
Individual evidence
- ↑ Mayer AM: Polyphenol oxidases in plants and fungi: going places? A review . In: Phytochemistry . 67, No. 21, November 2006, pp. 2318-2331. doi : 10.1016 / j.phytochem . 2006.08.006 . PMID 16973188 .