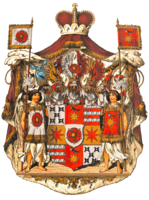
Coat of arms
The crests coat , as a pavilion or throne tent called, is a heraldic gem . It is an extended, magnificently designed cloak, which is held together at the top with a crown of rank and encloses a coat of arms . It was reserved for the princely arms of the high nobility . On the outside it is usually depicted in the heraldic colors red or purple. The inside of fur is properly an ermine . But other heraldic colors are also often used. The edges are decorated with golden fringes and golden tassel cords round off the coat of arms. Using the coat of arms instead of the helmet covers is unheraldic.
The coat of arms tent also encloses the entire coat of arms, i.e. pedestal , shield holder , coat of arms shield, etc. and is a crowned canopy . Another name is purple canopy . Its outer sides (inside and outside the same as the coat of arms) are often covered or sown with the main coat of arms. An example is the eagle in Prussia and the lily in France, which adorn the outside. King Friedrich I probably introduced the coat of arms in Prussia . Before that, however, it was already in use in France . The heraldic peculiarity has to be dated to around 1680.
In Napoleonic heraldry , the lilies on the gem were replaced by bees and, depending on the rank of nobility, draped and crowned with toque .
Coat of arms in the coat of arms of Johann Franz Eckher von Kapfing as Prince-Bishop of Freising
Individual proof
- ^ Milan boys : Heraldry . Albatros Praha, 1986