Pythagoras tree
A Pythagoras tree is a special type of fractal . The original method for creating a Pythagorean tree is based on the Pythagorean Theorem , in which two more, smaller squares are arranged at right angles on a square . By recursively calling this construction rule, a fractal is generated which, in the borderline case, resembles the shape of a tree. Due to the right angle of the enclosed triangle , the total area of each level remains the same, therefore the area of the basic element (trunk) is exactly as large as the sum of the area of all outer elements (leaves).
construction
 Image 1 |
 picture 2 |
 picture 3 |
 Picture 4 |
A square is constructed from a baseline. A Thales circle is drawn on the top of this basic element (trunk) and this is divided as desired. The resulting point is connected to the basic element (Fig. 1) so that a right-angled triangle is created. From each of the two legs of the triangle a square is constructed (Fig. 2) , a Thales circle is drawn, this is divided, a right-angled triangle is constructed (Fig. 3) and thus expanded to a square again (Fig. 4) . This process can be repeated as often as required.
Calculations on the right-angled and isosceles Pythagoras tree
height
The following is the side length of the first square (the "stem") . The height of the first (base) branch is, as seen in the first drawing . To determine the maximum height, it is sufficient to place branches of the shape shown on top of each other. Each branch has half the base of the previous branch. This is the height of the second branch , that of the third , etc. The total height is:
So:
width
The left branch corresponds to a transverse tree with the base side . Likewise the right branch. In the middle remains a trunk with the width and the two main branches each with the width . In order to:
Trunk length
To calculate the trunk length - red in the adjacent drawing - only the side lengths of the squares have to be added.
- Square:
- Square:
- Square:
- Square:
etc.
There is always the factor . If you start the numbering at 0, the following applies:
Side length of the -th square:
So the total length of the red line is:
Length of the treetop
To calculate the length of the treetop - blue in the drawing - first consider the following: You can get to the corners of the tree by walking along the branches alternately to the left and right. In order to calculate the length of the upper horizontal line, the deviation from the stem center line, which results from the growth of a right-left branch, is first calculated.
| Base side | Deviation from the center line |
|
|---|---|---|
| First right-left combination (square, triangle, square, triangle - dashed in the drawing) |
||
| Second right-left combination (dotted in the drawing) |
||
| Third right-left combination | ||
| i-th right-left combination (attention: renumbering: the first is now the zeroth!) |
The maximum deviation of the "last" peak from the first center line is then the sum of the individual deviations:
A left-right-left-right-… branch therefore deviates from the first center line at most. The same applies to the mirrored right-left-right-left-… branch. The two upper corners therefore have the maximum distance of . This is the length of the top horizontal blue line.
The lengths of the other blue lines can be easily calculated. The second blue line corresponds to the upper horizontal line of the main tree, etc.
| Base tree | length | |
|---|---|---|
| First blue line | ||
| Second blue line | ||
| Third blue line | ||
| i-th blue line (attention: renumbering: the first is now the zero!) |
Each blue line is three times longer than the corresponding red line. This means that the total length of the blue line is three times the red line:
scope
If you want to go around the tree once, you have to walk twice the blue and twice the red line and the line on which the tree stands. The upper blue line is double, so you have to subtract it once:
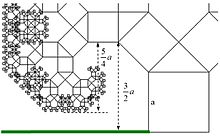
Distance to the lawn
In order to be able to drive the lawnmower up to the trunk, you have to know how high the clear height is under the foliage of the tree. So: how far is it from the lawn to the first leaves?
With a base side of is the total width . So one side of the tree protrudes beyond the trunk (length of the green line). To calculate the required clearance, consider the third branch - the first horizontally growing branch (or: third square):
The base side of this part of the tree is: . The width of this branch is therefore . With this branch, too, the crown protrudes by the factor , i.e . : . This third branch has a distance from the lawn of . The clear height is then the difference:
history
The Pythagoras tree was first constructed by Albert E. Bosman (1891–1961), a Dutch math teacher, in 1942.
Other forms
Since such a tree, which was created strictly according to Pythagoras, looks very unnatural, it is of course possible to deviate from the original form.
|
Pythagoras tree:
|
Fractal tree:
|
|
Pythagoras tree:
|
Pythagoras tree:
|
|
Pythagoras tree:
|
Pythagoras tree:
|
|
Pythagoras tree |
SW Pythagoras tree |
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ http://www.wisfaq.nl/show3archive.asp?id=32367&j=2005
- ↑ Archived copy ( Memento of the original from January 18, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Archived copy ( memento of the original from January 1, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.