Chest x-ray
The chest X-ray or the chest X-ray refers to an X-ray of the chest in a straight or side view (plane). It's a routine check-up. It is used to judge:
- lung
- Heart : size ( heart-thorax quotient , vertebral heart score ) and shape
- Mediastinum (middle part)
- Pleura (pleura)
- diaphragm
- bony chest with ribs , sternum (breastbone) and thoracic spine
Indications
A chest x-ray is suitable for clarifying / excluding the following diseases:
- Inflammation of the lungs ( pneumonia )
- Pneumothorax
- Pleural effusion ( hemothorax , chylothorax )
- Emphysema
Beam path
With a chest x-ray, there are different beam paths, i.e. different options for the direction from which the rays enter the body. The recordings are usually made using hard blasting technology.
- pa-projection (posterior-anterior): radiation source behind the thorax, detector / film in front of it (usually when the patient is standing)
- ap-projection (anterior-posterior): radiation source in front of the thorax, detector / film behind it (usually when the patient is lying down, e.g. in the intensive care unit. The other projection can make structures appear enlarged because they are closer to the radiation source If the total distance between the radiation source and the patient is smaller when taking pictures in bed, the result is greater magnification.)
- II projection (latero-lateral): lateral projection, lying either on the right or left with respect to the detector / film. This beam path is the most frequently used in veterinary medicine because the chest is "squeezed" sideways in animals.
In practice, the chest X-ray is usually recorded in two planes, namely p. a. and on the left. With these projections, the distortion of the heart shadow is relatively small compared to the other projections. In bed-ridden patients with a greatly reduced general condition, usually only one AP is performed.
Possible pathological changes
- Lung tumors , pulmonary edema , tuberculosis , sarcoid
- Pneumothorax , chylothorax
- Heart diseases such as pericardial effusion ( haematopericardium , chylopericardium ) or cardiomyopathies
- Diseases of the aorta (e.g. aneurysms )
- Diseases of the windpipe such as tracheal collapse
- Diseases of the esophagus such as megaesophagus
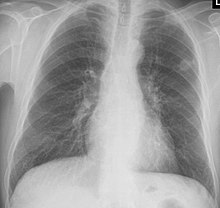
Example of a normal finding
p. a.-exposure while standing: the diaphragmatic crusts are smoothly delimited / bordered, the (lateral) recesses / marginal angles are free / visible. The lungs are transparent on both sides, ventilated on the same side and show no shadows. The heart is properly configured in shape, position and size. The Hili are vascular typical normal. The mediastinal shadow is central and not widened. The trachea is in the middle. The aortic button is regular. The pleura lies against the chest wall on all sides. The bony thorax and the soft tissue jacket are normal.
Lateral view: The retrosternal space and the retrocardial space are freely visible, as are the posterior recesses. The aortopulmonary window is not reduced in transparency.
Assessment: normal cardiopulmonary findings.
Web links
- Entry on chest x-ray in Flexikon , a wiki from DocCheck