Rubidium azide
| Crystal structure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
| __ Rb + __ N 1 / 3− | |||||||
| Crystal system |
tetragonal |
||||||
| Space group |
I 4 / mcm (No. 140) |
||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 630.8 pm, c = 753.7 pm, Z = 4 |
||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Rubidium azide | ||||||
| Ratio formula | RbN 3 | ||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, slightly hygroscopic crystals |
||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||
|
|||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Molar mass | 127.488 g · mol -1 | ||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| density |
2.79 g cm −3 |
||||||
| Melting point |
310 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Rubidium azide is a chemical combination of rubidium and nitrogen .
Manufacturing
Rubidium azide can be made from rubidium carbonate and sodium azide .
Rubidium azide is also formed by the action of nitrogen on rubidium under the influence of an electrical discharge. Rubidium nitride is produced in parallel .
properties
Physical Properties
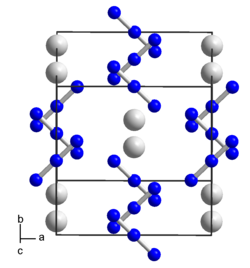
Rubidium azide crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system in the space group I 4 / mcm (space group no. 140) with the lattice parameters a = 630.8 pm, c = 753.7 pm, and 4 formula units per unit cell .
Chemical properties
The thermal decomposition of rubidium azide at 310 ° C produces rubidium nitride as well as elemental rubidium (60%). However, it's not explosive.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Pocket book for chemists and physicists. 3. Elements, inorganic compounds and materials, minerals, Volume 3. 4. Edition, Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-5406-0035-0 , p. 688 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ a b c Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: Handbook of inorganic compounds . CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-8671-8 , p. 333 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Dissertation: "Structural chemistry studies of halide azides of barium, thallium and zinc", University of Dortmund, 2001. PDF
- ↑ H. Wattenberg: About two modes of formation of sodium nitride and potassium nitride in Ber. d. German chem. Ges. 1930 , 63 (7), pp. 1667-1672. doi : 10.1002 / cber.19300630708 .
- ↑ Ulrich Müller: "Refinement of the crystal structures of KN 3 , RbN 3 , CsN 3 and TlN 3 " in Zeitschr. f. anorg. u. allg. Chem. 1972 , 392 (2), pp. 159-166. doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19723920207
- ^ Don M. Yost: "Systematic Inorganic Chemistry", Read Books Verlag, 2007. ISBN 978-1-4067-7302-6 . P. 128ff. ( limited preview in Google Book search)
- ^ R. Abegg, F. Auerbach: 'Handbuch der inorganic Chemie'. Verlag S. Hirzel, Vol. 2, 1908. P. 430. Full text


