Florida double snake
| Florida double snake | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Florida double worm ( Rhineura floridana ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the family | ||||||||||||
| Rhineuridae | ||||||||||||
| Vanzolini , 1951 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Rhineura | ||||||||||||
| Cope , 1861 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the species | ||||||||||||
| Rhineura floridana | ||||||||||||
| ( Baird , 1859) |
The Florida twin snake ( Rhineura floridana ) is the only species of the Rhineuridae family within the twin worm (Amphisbaenia). It is also the only double snake that can be found in eastern North America, its range is limited to the north and central Florida .
features
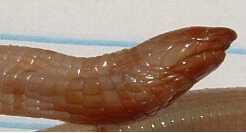
The Florida double sneak reaches an average length of 18 to 28 centimeters and can reach a maximum length of about 41 centimeters. Like all double snakes, it is serpentine and has no legs. The body is occupied by regular, rectangular body scales that are arranged in parallel and give the animal a segmented appearance. The coloring is uniformly flesh-colored.
The small head is separated from the body by a slight furrow and is clearly covered with larger scales . Both the head and the rear end are pointed. The lower jaw disappears in the upper jaw when the mouth is closed, making digging easier. There are no external ear openings, and in many individuals the eyes are open but not developed. The top of the very short tail is slightly flattened and covered with many small tubercles .
Due to the segmented body and the color, the double sneak can be mistaken for an earthworm on cursory inspection .
distribution and habitat
The Florida double worm is found only in north and central Florida. It was found that the northern populations differ genetically from the southern populations relatively strongly and that there are also greater genetic differences within the southern populations. This ensures that there is only little genetic exchange between the individual regions of the distribution area.
Way of life
The Florida double snake lives underground and digs tunnels with its body in loose earth or in dry sand. It feeds mainly on earthworms, soil insects such as beetle larvae, termites and ants as well as spiders.
Systematics
This species has been part of the monotypical family Rhineuridae within the double creeps since 2003, until that time it was considered a species within the actual double creeps (Amphisbaenidae). This view was confirmed by molecular data in 2004, and the species, the most original of all double-creeps, was compared to all the other species as sister species.
Hazard and protection
The Florida double snake is classified by the IUCN as not endangered ("Least Concern"). This assessment is based on the relatively large distribution area of the species, the insensitivity to ecological changes and the high estimated population.
supporting documents
Individual evidence
- ↑ J. Robert Macey, Theodore J. Papenfuss a. a .: Phylogenetic relationships among amphisbaenian reptiles based on complete mitochondrial genomic sequences. In: Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 33, 2004, p. 22, doi : 10.1016 / j.ympev.2004.05.003 .
- ↑ Rhineura floridana in the Red List of Threatened Species of the IUCN 2007. Posted by: Hammerson, GA, 2007. Accessed on 15/01/2008.
literature
- Roger Conant, Joseph T. Collins: A Field Guide to Reptiles & Amphibians. Eastern and Central North America. Peterson Field Guides, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston and New York 1998; Pages 280-281. ISBN 0-395-90452-8
