Sheet resistance
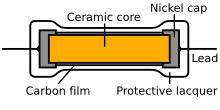
A sheet resistor is a type of electrical resistor and is characterized by a defined electrical resistance . The structure of the sheet resistor consists of an electrically non-conductive ceramic core as a carrier material, which is provided with a layer of carbon , a metal oxide, a metal glaze or a metal and two metal leads.
Approximate temperature coefficients :
- Coal layer :
- Metal layer :
High resistance values are achieved with the help of a helix , but the parasitic inductance increases. The electrical resistance value can be adjusted by grinding, sandblasting, electron beam or laser ablation. Most resistors are not matched, just sorted.
Depending on the frequency range and resistance value, the parasitic inductance and capacitance must be taken into account with sheet resistors . In the case of high-frequency applications, the inductance can usually be neglected for sheet resistances with values greater than 100 Ω ; the capacitance is of the order of 0.5 pF.
to form
A distinction is made between thin-film and thick-film resistors, depending on the production method of the layer . Depending on the design, a distinction is made between cylindrical and flat geometries, each wired for through-hole mounting or unwired for surface mounting .
Thin-film resistors are also manufactured as fuse resistors and interrupt the flow of current in the event of an overload without causing a fire.
Typical sheet resistance ranges of functional layers
| application | Main resistance area |
|---|---|
| Architectural glass (LowE) | 1 - 10 ohms / sq |
| Transparent electrodes in PV and smart glass | 5 - 50 ohms / sq |
| Transparent electrodes in OLED | 5 - 500 ohms / sq |
| Non-transparent metal electrodes | 0.1 - 1 ohm / sq |
| Displays | 10-1000 ohms / sq |
| Touch panel sensors (TPS) | 10-1000 ohms / sq |
| Packaging films | 0.001-3000 ohms / sq |
| Capacitor foils | 0.01-100 ohm / sq |
| Graphene layers | 30-3000 ohms / sq |
Parameters
In addition to the geometry, there are the following parameters:
- Resistance value and its tolerance
- Temperature coefficient
- Dielectric strength and voltage dependence of the resistance
- Operating temperature and load capacity (continuous and pulse power loss)
literature
- Otto Zinke : resistors, capacitors, coils and their materials . Springer Verlag, Berlin 1965, ISBN 978-3-540-03434-6 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Overview of typical sheet resistance ranges. Retrieved December 17, 2019 .