Black metrics
| Black metrics | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Uganda mangabe ( Lophocebus ugandae ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Lophocebus | ||||||||||||
| Palmer , 1903 |
The Black Meadows ( Lophocebus ) are a genus of primate from the family of vervet monkeys (Cercopithecidae). The genus includes six species that live in central Africa .
According to the latest findings, the white-eyed mangabians ( Cercocebus ) only superficially resemble the Schwarzm indications, but are not closely related, so that the " mangabies " do not represent a systematic group.
description
In contrast to the Weißlid-Mangaben, black-eyed figures have a black or black-gray fur . With a head body length of 40 to 72 centimeters, they are also smaller than this. The bushy tail becomes 55 to 100 centimeters long and their weight is 4 to 11 kilograms. In contrast to other cheekbones monkeys, the sexual dimorphism (males are larger than females) is less pronounced.
Distribution area and habitat
Black muzzles live in central Africa , their range extends from southeastern Nigeria to northern Angola , the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Tanzania . Their habitat is predominantly tropical rainforest ; they are mostly in the vicinity of water.
Way of life
These animals live almost exclusively on trees and rarely come to the ground. They are mostly located in the middle and upper area of the branches. Like all Old World monkeys, they are diurnal. Black mobs live in groups of 10 to 20 animals, which sometimes split up into smaller units while foraging for food. These groups consist of one or more males, numerous females and their offspring. Within the group, the animals communicate using a range of sounds and postures.
The animals are territorial and tell other groups their whereabouts by screaming. As a result of this understanding, there are seldom aggressive encounters between different groups.
food
Their diet consists of fruits, nuts and small animals. Sometimes they also invade plantations and consume the crops, this is the only reason for them to get on the ground.
Reproduction
After a gestation period of around 175 days, the female usually gives birth to a single young. The length of suckling is unknown, but there have been observations that other females in the group are also looking after the offspring. Females reach sexual maturity at three years of age, males at five to seven. While males have to leave their birth group at this point in time, females remain in the same group throughout their lives. The highest known age of an animal in human care was 32 years, in the wild life expectancy is certainly lower.
Danger
The threats to the Black Bulls include the destruction of their habitat by clearing forests and hunting when they devastate plantations. Overall, however, they are among the less threatened primates on the African continent.
The species
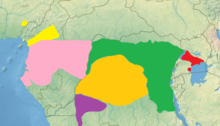
There are seven types:
- Mantle group, occurs north of the Congo Arch
- The gray cheek indication ( Lophocebus albigena ) is characterized by gray whiskers and gray, long shoulder hair. She lives in Gabon and the Republic of the Congo.
- The Johnston Mangabe ( Lophocebus johnstoni ) has a dark coat and lives in the north of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- The Uganda mangabe ( Lophocebus ugandae ) is similar to the gray-cheeked mandala, but is significantly smaller. It is endemic to Uganda.
- The Osman Hill Mangabe ( Lophocebus osmani ) has reddish-brown hair on its shoulders and lives on the Cameroon plateau.
- Schopfmdatengruppe, occurs south of the Congo Arch
- The Schopfm Detail ( Lophocebus aterrimus ) has a brownish whiskers and a pronounced head of hair. The species lives in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- The Opdenbosch mangabe ( Lophocebus opdenboschi ) lives in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and in Angola.
The Uganda-, the Osman-Hill and the Johnston-Mangabe have only been considered separate species since 2007, before they were combined with the gray-cheek indication as coat indication.
The Kipunji monkey , which was discovered in 2005 , also known as the Hochlandm declaration, was initially also included in the Schwarzm declaration, but according to recent studies it is classified in its own genus, Rungwecebus .
literature
- Thomas Geissmann : Comparative Primatology. Springer, Berlin 2003, ISBN 3-540-43645-6 .
- Colin Groves : The Endemic Uganda Mangabey (Lophocebus ugandae), and Other Members of the albigena-Group (Lophocebus). In: Primate Conservation. No. 22, 2007, pp. 123-128, doi : 10.1896 / 052.022.0112 .
- Ronald M. Nowak: Walker's Mammals of the World. 6th edition. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore 1999, ISBN 0-8018-5789-9 .