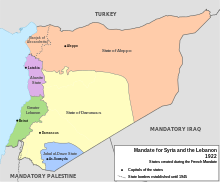
State of Damascus
The State of Damascus ( French État de Damas , Arabic دولة دمشق Daulat Dimaschq ) was one of the five states established by the French General Henri Gouraud as part of the League of Nations mandate for Syria .
history
After the Sanremo Conference and the defeat of King Faisal's monarchy over Syria , the state of Damascus was proclaimed by General Gouraud on September 3, 1920. The state of Damascus included Damascus as its capital and the surrounding region as well as the Nahr al-Asi valley with the cities of Homs and Hama . The first president of the new state was Hakki Bey al-Azm .
Damascus state lost four qadas (sub-districts) that were part of Vilayet Syria during the Ottoman rule . The territory corresponds roughly to that of the Bekaa plain and southern Lebanon . Together with the predominantly Christian Lebanonberg , the new state Greater Lebanon emerged from it. Damascus and the predominantly Muslim population of the region protested against the secession of the Qadas throughout the mandate, and the later Syrian Republic also repeatedly demanded the territories back.
On June 22, 1922, General Gouraud finally announced the establishment of the Syrian Federation ( la Fédération Syrienne ). This initially included the state of Damascus, Aleppo and the Alawite state . In 1924 the Alawite state was split off again, and the Syrian Federation became the new state of Syria on December 1, 1924 .