Tecovirimate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
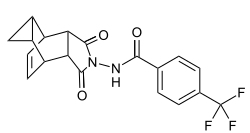
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Tecovirimate | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 15 F 3 N 2 O 3 | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 376.34 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Tecovirimate is an antiviral agent that is effective against orthopoxviruses . Representatives of this family of viruses solve diseases such as smallpox and monkeypox from.
Tecovirimat is approved in the USA - as the only active ingredient to date - against smallpox. So far, the agent has only been used once to treat a woman who was infected in a laboratory.
Tecovirimat was developed as an antidote for smallpox viruses in order to be prepared for a possible use of this pathogen as a biological warfare agent. Two million doses of tecovirimate are held in US national strategic supplies in the event of an attack by a smallpox virus-based chemical weapon (bio-warfare agent attack).
The active ingredient blocks the cellular transmission of the virus. Tecovirimate was effective in laboratory tests: it protected animals from monkey and rabbit pox . The safety for humans was examined in 359 healthy volunteers without smallpox infection. The most common side effects were headache, nausea, and abdominal pain.
Clinical studies
The results of clinical studies on tecovirimate support the belief that it is effective against smallpox and other related pathogens. It showed potential effectiveness against various variations including prophylaxis and can be used as a supplement to vaccination.
Tecovirimat was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is now allowed to conduct Phase II trials. In phase I trials, tecovirimate generally worked without significant difficulties or side effects. Because of its importance in defense against bio-warfare agents, the FDA has given tecovirimate fast-processing status, so ways for preferential investigation by the FDA have been created around regular approval. On July 13, 2018, the FDA announced the approval of Tecovirimate.
Mechanism of action
Tecovirimate inhibits the activity of the viral protein p37, which in orthopoxviruses is involved in the formation of the virus envelope and the release of viruses from the infected cells. By suppressing the formation of virions , it prevents the virus from spreading throughout the body.
development
Tecovirimate was originally discovered at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and further researched by Viropharma in collaboration with scientists from the United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). It is now being produced by Siga Technologies , a pharmaceutical company that conducts research into defense against biological weapons and developed the drug under an official contract following a US tender.
Finished medicinal products
Approval in the USA as Tpoxx (Siga Technologies)
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Office of the Commissioner: Press Announcements - FDA approves the first drug with an indication for treatment of smallpox. Retrieved October 12, 2018 .
- ↑ https://www.focus.de/gesundheit/news/absterbendes-haben-labormitarbeiterin-infiziert-sich-mit-pocken-virus-galt-seit-1980-als-ausgerottet_id_11401552.html
- ^ Inger K. Damon, Clarissa R. Damaso, Grant McFadden: Are We There Yet? The Smallpox Research Agenda Using Variola Virus . In: PLoS Pathogens . tape 10 , no. 5 , May 1, 2014, doi : 10.1371 / journal.ppat.1004108 , PMID 24789223 , PMC 4006926 (free full text).
- ↑ Aimee Cunningham: FDA approves the first smallpox treatment . In: Science News . July 13, 2018 ( sciencenews.org [accessed October 12, 2018]).
- ↑ Office of the Commissioner: Press Announcements - FDA approves the first drug with an indication for treatment of smallpox. Retrieved October 12, 2018 .
- ↑ Guang Yang, Daniel C. Pevear, Marc H. Davies, Marc S. Collett, Tom Bailey: An Orally Bioavailable Antipoxvirus Compound (ST-246) Inhibits Extracellular Virus Formation and Protects Mice from Lethal Orthopoxvirus Challenge . In: Journal of Virology . tape 79 , no. 20 , October 2005, p. 13139-13149 , doi : 10.1128 / JVI.79.20.13139-13149.2005 , PMID 16189015 , PMC 1235851 (free full text).