Toric lens
A toric lens is a lens that has two different refractive powers in two mutually perpendicular directions . At least one of the lens surfaces has the shape of a "cap" of a torus (see Fig. 1), the other is mostly spherical . Toric lenses are used for glasses , as contact lenses and intraocular lenses to correct astigmatism . It can also be used to bundle laser beams into elliptical foci .
Torus
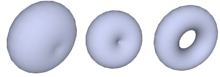
A torus is created when a circle with a radius rotates around an axis ( -axis in Fig. 2) that lies in the same plane as the circle. The center of this circle follows a circular path with a radius around the axis of rotation. If so, you get a ring torus . If so, the opening has shrunk to the center of the circle of revolution; one speaks here of a horn torus . If so, one speaks of a spindle torus ; here only two depressions remain of the opening, the depth of which disappears when you go. If so, the torus has degenerated into a sphere with the radius . (See Fig. 3.)
description
The largest radius of curvature of the toric lens surface is (see Fig. 2); the corresponding smallest refractive index is when the refractive index of the glass is. The smallest radius of curvature , corresponding to the largest refractive power . There is is . The difference ,, is called the cylinder correction in ophthalmology and optics . The glass behaves roughly like a combination of a spherical lens with the refractive power and a cylindrical lens with the refractive power .
The maximum and minimum curvature are both circular - so the lens surface is by no means part of an ellipsoid of revolution, as is sometimes claimed.
effect
Light rays incident in the ( ) plane of the torus (see Fig. 2) are refracted according to the largest radius of curvature, i.e. the smallest refractive index .
Light rays in a plane through the -axis of the torus (see Fig. 2) are refracted according to the smallest radius of curvature, i.e. the greatest refractive index .
There are thus two different refractive indices in perpendicular directions. In the intermediate directions, the refractive power runs smoothly from the smallest to the largest value or vice versa. This compensates for the astigmatic deviations of the eye.
If parallel rays of light (laser, sun) are bundled with such converging lenses, elliptical foci arise depending on the distance.
Atoric lens
Computer-controlled design, grinding and polishing processes make it possible today to achieve good corrections in a larger field of view by introducing certain deviations from the torus shape. In this case one speaks of an atoric lens.
Individual evidence
- ↑ In terms of mathematics, one would rather expect the term toroidal lens . In the field of ophthalmology and optics, however, the term toric lens is common. Presumably this is based on the fact that in English the term torus only means the solid of revolution of a circle and the term toroid is only used for the solid of revolution of other flat figures.
- ↑ This corrects the astigmatism of the eye. The term cylinder is based on a mathematical approximation that is only valid for small correction values.
- ↑ D. Meister: Principles of Atoric Lens Design. In Lens Talk , Vol. 27, No. 3, 1998 ( PDF )
- ↑ D. Volk: Aspheric Lenses ( Memento of the original from March 12, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. . (chapter 50 in Duane's Ophthalmology (Lippinkott, Wilkins & Williams / Wolters-Kluwer Health, Chicago, USA))