Tricarboxylic acids
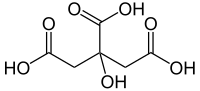
Structural formula of citric acid , one of the most famous representatives of this group

Structural formula of trimesic acid
Tricarboxylic acids are carboxylic acids that have three carboxy groups (–COOH). Carboxylic acids with only one carboxy group are called monocarboxylic acids , with two as dicarboxylic acids . Tricarboxylic acids are all compounds with three acid groups without defining the rest of the structure of the molecule.
Tricarboxylic acids, like many dicarboxylic acids, can form carboxylic acid anhydrides with intramolecular elimination of water .
The citric acid , the aconitic acid , the isocitric acid , and oxalosuccinic acid are intermediates in carbohydrate metabolism ( citric acid cycle ).
Examples
Individual evidence
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 6: T-Z. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1988, ISBN 3-440-04516-1 , p. 4340.