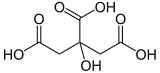
Isocitric acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without stereoisomerism | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Isocitric acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 8 O 7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, crystalline powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 192.13 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Isocitric acid is a colorless, water-soluble solid . It is a constitutional isomer of citric acid . The salts are the isocitrates.
If “isocitric acid” is mentioned in this article or in the scientific literature without further information on stereochemistry, the naturally occurring L - threo -isocitric acid, also (+) - isocitric acid or (2 R , 3 S ) -isocitric acid - a metabolic intermediate in the citric acid cycle - meant. The other three stereoisomers are only of secondary importance.
properties
Isocitric acid is counted among the organic tricarboxylic acids (see carboxylic acid ) due to its three carboxy groups (-COOH) . In addition, the hydroxy group (-OH) in position 2 of the carbon backbone identifies it as a hydroxycarboxylic acid . It differs from citric acid in the position of this hydroxyl group, which is in position 3 in citric acid.
Isomerism
3-carboxy-2-hydroxypentane-1,5-diacid is chiral and has two differently substituted stereocenters, i. that is, there are four distinguishable stereoisomers .
The naturally occurring L - threo -isocitric acid is also called
- (2 R , 3 S ) -3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-pentane-1,5-diacid,
- (2 R , 3 S ) -isocitric acid or
- (+) - isocitric acid
designated.
| Isomers of isocitric acid | ||||
| Surname | L - threo -isocitric acid | D - threo -isocitric acid | D - erythro -isocitric acid | L - erythro -isocitric acid |
| other names | (+) - threo -isocitric acid (2 R , 3 S ) -isocitric acid (1 R , 2 S ) -1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
(-) - threo -Isocitric acid (2 S , 3 R ) -Isocitric acid (1 S , 2 R ) -1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
(-) - erythro -isocitric acid (2 S , 3 S ) -isocitric acid (1 S , 2 S ) -1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
(+) - erythro -isocitric acid (2 R , 3 R ) -isocitric acid (1 R , 2 R ) -1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
| Structural formula |
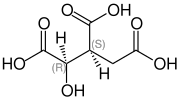
|

|
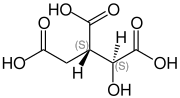
|

|
| CAS number | 6061-97-8 | 55582-48-4 | 30810-51-6 | 1187-17-3 |
| 18979-21-0 ( DL - threo -isocitric acid) | 344-79-6 ( DL - erythro -isocitric acid) | |||
| 320-77-4 (unspec.) | ||||
| EC number | - | - | - | - |
| 206-282-3 (unspec.) | ||||
| ECHA info card | - | - | - | - |
| 100.005.713 (unspec.) | ||||
| PubChem | 440409 | 5318532 | 447805 | 439238 |
| 1198 (unspec.) | ||||
| DrugBank | - | - | - | - |
| DB01727 (unspec.) | ||||
| Wikidata | Q27114011 | Q27105259 | Q27104505 | Q66723041 |
| Q288927 (unspec.) | ||||
Occurrence
The isocitric or their salts which are Isocitrate, an intermediate in carbohydrate - metabolism of all oxygen consuming living things , including humans . The metabolic sequence (see biochemistry ) is called the citric acid cycle .
It occurs in apples, pears, raspberries, blackberries, and currants.
Manufacturing
Large-scale production has not yet been established, neither of the racemate nor of a specific stereoisomer. With the help of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica , however, it was possible to produce (2 R , 3 S ) -isocitrate from refined sunflower oil in larger quantities and in a favorable ratio of isocitrate to citrate . After the biomass has been filtered off, the two components are obtained via electrodialysis and separated via an esterification , in which the citric acid ester crystallizes and the isocitric acid ester remains liquid.
physiology
(2 R , 3 S ) -Isocitrate is an intermediate product of several metabolic pathways in all living things. With the help of aconitase , it is created in a low concentration from citrate (via cis - aconitate as an intermediate) as part of the citric acid cycle .
Isocitrate is processed further
- from isocitrate dehydrogenase to alpha-ketoglutarate , in the citric acid cycle
- with the help of isocitrate lyase to glyoxylate and succinate , as part of the glyoxylate cycle of bacteria , or in the glyoxysomes of plants, fungi, algae and protozoa.
- to 2-caffeoyl isocitrate, catalyzed by a special enzyme ( EC 2.3.1.126 ) in Amaranthus species
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet DL-Isocitric acid, trisodium salt hydrate, 95% from Acros, accessed on February 20, 2010.
- ↑ a b Data sheet DL-Isocitric acid trisodium salt hydrate, ≥93% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 17, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Heretsch, Thomas, Aurich, Krautscheid, Sicker & Giannis (2008). Syntheses with a chiral building block from the citric acid cycle: (2 R , 3 S ) -isocitric acid from a fermentation with sunflower oil. Angewandte Chemie , 120; doi : 10.1002 / anie.200705000 .
- ^ Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, p. 365, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ↑ Heretsch, Thomas, Aurich, Krautscheid, Sicker & Giannis (2008). Syntheses with a chiral building block from the citric acid cycle: (2 R , 3 S ) -isocitric acid from a fermentation with sunflower oil. Angewandte Chemie , 120; doi : 10.1002 / anie.200705000 .