Trios
Trioses are the simplest monosaccharides with three carbon atoms in the carbon backbone. They all have the empirical formula C 3 H 6 O 3 and differ in the type of carbonyl function. If it is a keto group , then one speaks of ketoses , in the case of an aldehyde group it is called aldoses . The trios do not occur freely in the organism, but the phosphoric acid esters play an important role in the carbohydrate metabolism.
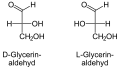
The aldotriose glyceraldehyde has a chiral center , so there are two stereoisomeric forms . The ketotriose dihydroxyacetone has no chiral center.
Structure of all trios
Position in metabolism
Gluconeogenesis in carbon dioxide assimilation : Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (abbreviated as GAP or G3P) is formed in the Calvin cycle of the chloroplasts of plants . From the triosephosphate are monosaccharides formed.
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Brockhaus ABC Chemie , VEB FA Brockhaus Verlag, Leipzig 1965, p. 1438.
Web links
- Uni Erlangen: trios