Treaty of Bangkok
| Contract (from) | region | Signatory / ratification |
Year signed / in force |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antarctic Treaty | Antarctic | 45/45 | 1959/1961 |
| Tlatelolco | Latin America / Caribbean | 33/33 | 1967/1968 |
| Rarotonga | South pacific | 13/13 | 1985/1986 |
| Two-plus-four contract | former GDR and Berlin | 6/5 * | 1990/1991 |
| Mongolia Nuclear Weapon Free Zone | Mongolia | 1/1 | 1992/2000 |
| Bangkok | South East Asia | 10/10 | 1995/1997 |
| Pelindaba | Africa | 53 (54) / 40 | 1996/2009 |
| Semei | Central Asia | 5/5 | 2006/2009 |
| * ratified by all still existing contracting parties (the GDR no longer existed) | |||
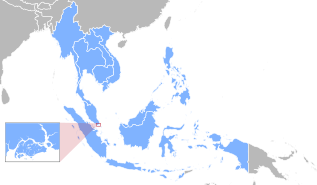
In the Treaty of Bangkok ( Treaty on the Southeast Asia Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone or Bangkok Treaty ), the ASEAN states undertake not to use nuclear weapons against each other or to threaten one another with their use.
prehistory
The roots of the Bangkok Treaty lie in the desire of the ASEAN states to meet all political , economic and security challenges together. This endeavor is already rooted in the Cold War .
signing
On December 15, 1995, the contract was signed in Bangkok by the ASEAN states Brunei , Indonesia , Malaysia , the Philippines , Singapore , Thailand and Vietnam . Laos , Cambodia and Myanmar also signed . On March 28, 1997, the contract finally came into force.
Web links
- Contract text (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ ASEAN | ONE VISION ONE IDENTITY ONE COMMUNITY. Retrieved May 25, 2017 (American English).
- ↑ B texts | Nuclear weapons AZ. Retrieved May 25, 2017 .
- ^ Southeast Asian Nuclear-Weapon-Free-Zone (SEANWFZ) Treaty (Bangkok Treaty) | Treaties & Regimes | NTI. Retrieved May 25, 2017 .