Victor Meyer reaction
The Victor Meyer reaction is a name reaction from organic chemistry . It was developed around 1872 by the German chemist Victor Meyer (1848–1897). This reaction is a substitution reaction .
Overview reaction
A haloalkane (e.g. 1-halobutane) reacts with silver nitrite in the heat to form a nitro compound :
General
This reaction is usually carried out with ether as the solvent and at temperatures around 80-110 ° C. Both a nitro group and a nitrite group are formed . The proportions of the respective groups depend on the type of haloalkanes and the nitrite metal compound. The yield of the nitro groups is falling from primary to tertiary haloalkanes, the opposite applies to the nitrite group. In addition, two different mechanisms take place in this reaction, the S N 1 and S N 2 mechanisms. It was also proven that in an S N 1 reaction, the bond to the more electronegative atom is much more likely and thus nitrite groups are more likely to arise. However, the yield ratios depend not only on electronic, but also on steric effects. For example, the CO bond of the nitrite group has less steric hindrance than the CN bond of the nitro compound. The two different nitrogen compounds can be separated by washing with concentrated sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid , since the nitrite group is not stable in an acidic medium. Despite the relatively low yield, this is one of the simplest and most useful methods to prepare nitroalkanes that have at least one butane radical or longer radicals.
Proposed reaction mechanism
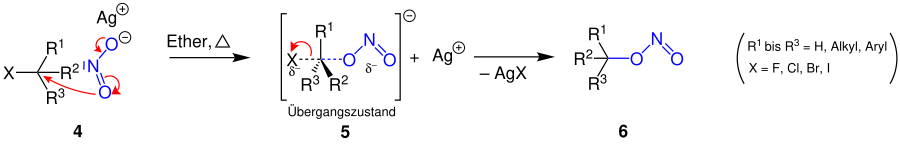
The reaction mechanism proposed here follows the S N 2 mechanism. A nucleophilic attack on the rear side of the haloalkane 1 takes place . In the following step, a transitional state 2 that is only present for a short time arises . Thereby an inversion ( Walden reversal ) takes place, i. H. the configuration of the atoms attached to the carbon changes (see Fig.). From step 2 to 3 the halogen splits off and precipitates with the silver cation as a salt (e.g. as silver chloride , silver bromide ). The end product is the nitroalkane 3 . The positive and negative charge in this molecule is based on the octet rule .
In addition, the nucleophilic attack by oxygen can take place in this reaction, whereby a flip of electrons from nitrogen to oxygen ensures a charge balance and we thus obtain a nitrite alkane 6 .
In general, hydrogen , aryl groups and alkyl groups function as radicals .
particularities
This reaction can also be carried out with sodium nitrite or potassium nitrite (instead of silver nitrite).
literature
- The Merck Index, 9th Edition, Merck & Co. 1976, ONR-60, ISBN 0-911910-26-3
- Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents , Volume 3, Wiley, 2009, pp. 2868-2871, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8
Individual evidence
- ^ Victor Meyer: Annalen der Chemie . tape 171 , 1884, p. 1-64 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18741710102 .
- ^ Nathan Kornblum, Bernard Taub, Herbert E. Ingnade: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 76 , 1954, pp. 3209 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01641a029 .
- ^ Nathan Kornblum, Robert A. Smiley, Robert K. Blackwood, Don C. Iffland: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 7 , 1955, pp. 6269-6280 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01628a064 .
- ^ A b Nathan Kornblum, Robert A. Smiley, Robert K. Blackwood, Don C. Iffland: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 7 , 1955, pp. 6269-6280 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01628a064 .
- ↑ a b c Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 2868-2871 .