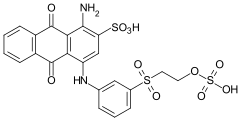
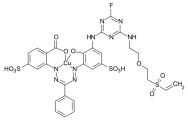
Vinyl sulfone dyes
Vinyl sulfone dyes are reactive dyes that have a vinyl sulfone group (VS group) as a reactive group (reactive anchor ). Due to the relatively high reactivity of the vinyl sulfone group towards water (residual moisture, atmospheric humidity), it is in a protected form in many commercial products. One ethylsulfonyl group is substituted with a leaving group . During the dyeing process under alkaline conditions, the VS group is released through an elimination reaction:
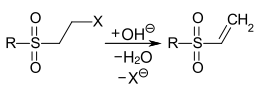
Generation of the vinyl sulfone group by alkaline elimination. R = alkyl or aryl radical , X = -OSO 3 H, -Cl
Chemical structure
The vinyl sulfone reactive anchor is usually introduced into the reactive dye via an aromatic or aliphatic amine .
The oldest and most common intermediate is the parabase ester , an aniline substituted with a [2- (sulfooxy) ethyl] sulfonyl group . Parabase ester can be used as a diazo component in the manufacture of azo dyes . Another possible reaction is the condensation reaction of parabase ester with a chlorine or fluorotriazine radical, which in turn is linked to any chromophore via a further amino group.
Possible variations result from further substituents on the aromatic ring - mostly hydroxyl , methyl or methoxy groups , or from the position of the amino to the VS group. In addition to the para-substituted compound, meta- and ortho -substituted vinylsulfonanilines are also used.
If the VS group is introduced via a primary or secondary aliphatic amine, this is also done by condensation with a halotriazine compound. An example is 2- [2- (2-chloroethylsulfonyl) ethoxy] ethanamine, which is used in bifunctional reactive dyes in combination with a monofluoro or monochlorotriazine anchor.
Dyeing process
The vinyl sulfone group reacts with the nucleophilic functional groups of the fibers in the sense of a Michael addition with the formation of a covalent ether bond:

Reaction of vinyl sulfone compounds with the hydroxyl groups of cellulose
An undesirable side reaction in the dyeing process is the conversion of the VS group to the 2- (hydroxy) ethylsulfonyl group:

Reaction of the vinyl sulfone compounds with water / OH - as an undesirable side reaction during dyeing
The unreactive dye must be washed out during the aftertreatment of the dyeing.
history
The first dyes having a [2- (sulfooxy) ethyl] sulfonyl group were in 1949 by the former Farbwerke Hoechst patented and in the following years as wool dyes under the brand name Remalan , or as cotton dyes under the brand name Remazol marketed. From the early 1980s, reactive dyes, which in addition to the VS reactive group, have another monochlorotriazine anchor , were produced by the dye manufacturers Sumitomo (brand name Sumifix Supra ) and Hoechst AG. In 1988, Ciba-Geigy launched double anchor dyes with a combination of a VS reactive group and a monofluorotriazine reactive group under the brand name Cibacron .
Examples
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on reactive anchors. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 4, 2019.
- ↑ a b Patent DE965902 : Process for fixing water- soluble organic compounds on substrates with a fibrous structure. Registered on July 19, 1949 , published on September 19, 1957 , applicant: Hoechst AG, inventor: Johannes Heyna, Willy Schumacher.
- ^ E. Siegel: Reactive Groups . In: K. Venkataraman (Ed.): The Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes . tape VI . Academic Press, New York, London 1972, pp. 36 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Patent EP0775731 : Reactive dyestuffs, process for their preparation and use thereof. Published on May 28, 1997 , applicant: Ciba Geigy, inventor: Urs Lehmann, Marcel Frick.
- ↑ The reaction of VS reactive dyes with water is also referred to in the literature as "hydrolysis", see: ID Rattee: Reactive Dyes - Physicochemical Aspects of Dye Fixation and Dye-Fiber Bond Hydrolysis . In: K. Venkataraman (Ed.): The Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes . tape VIII . Academic Press, New York, London 1978, ISBN 0-12-717008-1 , pp. 2 ff .
- ↑ Klaus Hunger (Ed.): Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, Properties, Applications . WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 978-3-662-01950-4 , p. 113, 117–118 ( limited preview in Google Book search).