Warner Scarab
| Warner Aircraft Corporation | |
|---|---|
|
Scarab 110 |
|
| Scarab / SuperScarab | |
| Production period: | 1928-1940s |
| Manufacturer: | Warner Aircraft Corporation |
| Developing country: |
|
| First run: | November 1927 |
| Working principle: | Otto |
| Motor design: | Radial engine |
| Displacement: | 6920 cm 3 |
| Mixture preparation: | Carburetor |
| Engine charging: | no |
| Power: | 93-138 kW |
| Previous model: | none |
| Successor: | none |
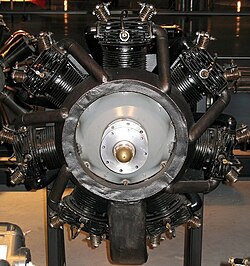
The Warner Scarab is a radial aircraft engine that was built by Warner Aircraft Corporation in Detroit from 1928 to the 1940s. Its military designation is R-420.
Versions
- Scarab S-50
- Air-cooled seven-cylinder radial engine, introduced in 1928. With a cylinder bore and a piston stroke of 108 mm and a compression ratio of 5.2: 1, the Scarab develops 125 hp (92 kW ) at 2050 revolutions per minute from a displacement of around seven liters . Its dry weight is 129 kilograms.
- Scarab Junior
- Version with five cylinders, presented in 1930, 90 hp (66 kW) at 2125 revolutions per minute from a displacement of around five liters with a dry weight of 104 kilograms

- Super Scarab SS-50 / 50A
- With a bore enlarged to 117.5 mm, it develops 145 hp (107 kW) at 2050 revolutions per minute from a displacement of eight liters, dry weight 137 kilograms.
- Super Scarab SS-165
- Increase in performance through improved compression ratio (6.4: 1) to 165 HP (121 kW) at 2100 revolutions per minute, dry weight 155 kg
- Super Scarab SS-185
- Increase in output through enlarged cylinder bore (123.8 mm) to 185 HP (136 kW) at 2175 revolutions per minute, dry weight 156 kg
- R-420
- Military name of the Scarab
- R-500
- Military name of the Super Scarab 165
- R-550
- Military name of the Super Scarab 185
- 145
- Alternative name of the Super Scarab SS-50 / 50A
- 165
- Alternative name of the Super Scarab 165
- 185
- Alternative name for the Super Scarab 185 (mainly used in helicopters ).
use
Among other things, the Scarab was installed in the Cessna 165 Airmaster and the Fairchild 24 . It was also used to power the Sikorsky R-4 , the first helicopter to be mass-produced in the United States.
Mainly because of the high availability of spare parts due to its use in the Fairchild UC61 and Meyers OTW during World War II , many of these reliable units are still running today in the aircraft in which they were originally installed. The 145 PS (107 kW) and 165 PS (121 kW) engines were the most common engines in US aircraft from before World War II. In addition, the engines are often used for replicas and restorations of aircraft from the First World War.
List of aircraft equipped with Warner-Scarab engines
- CAC Wackett
- Cessna 165 Airmaster
- Cessna Model AW
- Curtiss XC-10
- Davis D-1
- Fairchild 22 C7E, C7F
- Fairchild 24 C8B
- Fleet Model 1
- General Aristocrat
- Gee Bee Sportster
- Harlow PJC-2
- L-class blimp
- Meyer's OTW
- Monocoupe 110
- Pasped Skylark
- Redfern Nieuport 17/24
- Ryan SC
- Ryan ST-W
- Sands Fokker Dr.1 Triplane
- Sikorsky R-4
- Stinson SM-2
- Waco RSO
- Waco RBA
- Waco BNF and RNF
Technical data (Scarab 50)
General data
- Type: Air-cooled seven-cylinder star engine
- Bore: 108 mm
- Stroke: 108 mm
- Displacement: 6.92 liters
- Length: 740 mm
- Diameter: 928 mm
- Height: 930 mm
- Dry weight: 132 kg
Components
- Valves: Two per cylinder
- Mixture preparation : NA-5SA Stromberg carburetor
- Fuel type: AvGas with 67 octane
- Lubrication : dry sump
- Cooling: air
Performance data
- Power: 125 PS (92 kW)
- Compression: 5.15: 1
- Specific fuel consumption : 334 g / kWh
- Specific oil consumption: 15 g / kWh
- Power-to-weight ratio : 1.434 kg / kW