Yanomam languages
The Yanomam or Yanomamö languages are an indigenous language family of South America in the border area of Brazil (Roraima) and Venezuela (Amazon). The Yanomam languages include four closely related languages (the language code according to ISO 639-3 is given in square brackets ):
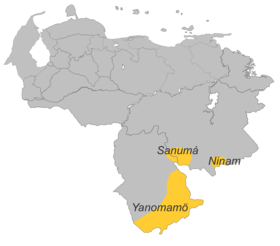
- Yanam (also: Ninam, Yanam-Ninam) [shb] (approx. 570 Yanam or Ninam speak Yanam / Ninam, of which approx. 470 in Brazil (1976) and approx. 100 in Venezuela, some groups in Venezuela also speak the pemón of the neighboring Pemón and Spanish)
- Northern Yanam / Ninam (Shiriana, Uraricaa-Paragua, Xiliana , pronounced: 'Shi-ri-a-na') [shb-nor]
- Southern Yanam / Ninam (Shirishana, Mukajai, Xilixana , read: 'Shi-ri-sha-na') [shb-sou]
- Sanumá (also: Tsanuma, Sanïma) [xsu] (approx. 6,410 Sanema speak Sanumá, of which 4,610 in Venezuela (2000) and 1,800 in Brazil (2006 D. Borgman), some groups in Venezuela also speak Maquiritari [mch] of the neighboring Ye 'kuana )
- Yanoma (Kohoroxitari) [xsu-yan]
- Cobari (Kobali, Cobariwa) [xsu-cob]
- Caura [xsu-cau]
- Ervato-Ventuari [xsu-erv]
- Auaris [xsu-aua]
- Yanoma (Samatari, Samatali, Xamatari, “Kohoroxitari”)
- Yanomámi (also: Yanomam, Waiká) [wca] (approx. 9,000 Waika speak Yanomámi, is very similar to Yanomamö the actual Yanomami)
- Yanamam (Patimitheri, Waika) [wca-yan]
- Yanomam (Naomam, Guadema, Wadema, Warema) [wca-yao]
- Yanomay (Toototobi) [wca-yay]
- Nanomam (Karime) [wca-nan]
- Jauari (Joari, Yoari, Aica) [wca-jau]
- Yanomamö (also: actual Yanomamï, Guaharibo) [guu] (approx.17,640 Yanomami speak Yanomamö, is very similar to Yanomámi the Waika )
- Western Yanomami (Padamo-Orinoco) [guu-wes]
- Eastern Yanomami (Parima) [guu-eas]
The total number of speakers is 34,000, of which the Yanomamö ( actual Yanomamï) is the most important within the language family with 17,640 speakers.
Alternatively, this language family is also viewed as a dialect continuum , i.e. H. as a single language .
Linguistic characteristics
These are polysynthetic ergative languages with the basic word order subject-object-verb (SOV). They are also characterized by the presence of nominal classes . The sound systems are relatively simple. a. two central vowels [ɨ] and [ə].
See also
swell
- RMW Dixon , Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald (Eds.): The Amazonian languages . Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1999, ISBN 0-521-57021-2 , pp. 341-351.
- Helmut Glück (Ed.): Metzler Lexicon Language. Metzler, Stuttgart et al. 1993, ISBN 3-476-00937-8 .
- Harald Haarmann : Small Lexicon of Languages. From Albanian to Zulu (= Beck series. 1432). Beck, Munich 2001, ISBN 3-406-47558-2 .
- Marie-Claude Mattei Müller: Diccionario ilustrado yanomami-español, español-yanomami. Epsilon Libros, Caracas 2007.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Kohoroxitari is a village name and roughly means 'place of worms'