Zeisel test
The Zeisel test or Zeisel method was developed in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Simon Zeisel (1854–1933). This method is used for the analytical determination of alkoxy groups in ethers or esters .
application
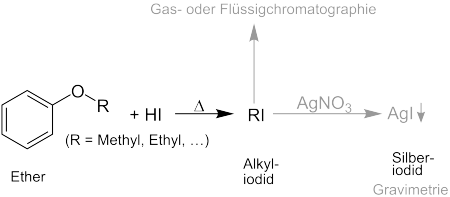
To determine the alkoxy groups (mostly methoxy and ethoxy ), the alkyl radical is first split off from the ether or ester with boiling hydroiodic acid (HI). The resulting alkyl iodide (RI) is distilled into a silver nitrate solution (AgNO 3 ) . This creates silver iodide , which can be determined gravimetrically .
The alkyl iodide can also be determined by gas or liquid chromatography .
Individual evidence
- ^ Entry on Zeisel method. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 19, 2020.
- ^ Zerong Wang: Comprehensive organic name reactions and reagents . John Wiley, Hoboken, NJ 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-63885-9 , pp. 3115-3117 , doi : 10.1002 / 9780470638859.conrr42 .