RAID
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2007) |
RAID — which stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (as named by the inventor) or Redundant Array of Independent Disks (a name which later developed within the computing industry) — is a technology that employs the simultaneous use of two or more hard disk drives to achieve greater levels of performance, reliability, and/or larger data volume sizes.
The phrase "RAID" is an umbrella term for computer data storage schemes that can divide and replicate data among multiple hard disk drives. RAID's various designs all involve two key design goals: increased data reliability and increased input/output performance. When several physical disks are set up to use RAID technology, they are said to be in a RAID. This array distributes data across several disks, but the array is seen by the computer user and operating system as just one, single disk. RAID can be set up to serve several different purposes, the most common of which are outlined below.
Purpose and basics
A RAID distributes data across several physical disks which look to the operating system and the user like a single disk. Several different arrangements are possible. We assume here that all the disks are of the same capacity, as is usual.
Some arrays are "redundant" in a way that writes extra data derived from the original data across the array organized so that the failure of one (sometimes more) disks in the array will not result in loss of data; the bad disk is replaced by a new one, and the data on it reconstructed from the remaining data and the extra data. A redundant array obviously allows less data to be stored; a 2-disk RAID 1 array loses half of its capacity, and a RAID 5 array with several disks loses the capacity of one disk.
Other RAIDs are arranged in a way that makes them faster to write to and read from than a single disk.
There are various combinations of these approaches giving different trade offs of protection against data loss, capacity, and speed. RAID levels 0, 1, and 5 are the most commonly found, and cover most requirements.
RAID 0 distributes data across several disks in a way which gives improved speed and full capacity, but all data on all disks will be lost if any one disk fails.
RAID 1 (mirrored disks) uses two (possibly more) disks which each store the same data, so that data is not lost so long as one disk survives. Total capacity of the array is just the capacity of a single disk. The failure of one drive, in the event of a hardware or software malfunction, does not increase the chance of a failure or decrease the reliability of the remaining drives(second, third, etc).
RAID 5 combines three or more disks in a way that protects data against loss of any one disk; the storage capacity of the array is reduced by one disk. The less common RAID 6 can recover from the loss of two disks.
RAID involves significant computation when reading and writing information. With true hardware the RAID controller does the work. In other cases the operating system or simpler and less expensive controllers require the host computer's processor to do the computing, which reduces the computer's performance on processor-intensive tasks (see "Software RAID" and "Fake RAID" below). Simpler RAID controllers may provide only levels 0 and 1, which require less processing.
RAID systems with redundancy continue working without interruption when one, or sometimes more, disks of the array fail, although they are vulnerable to further failures. When the bad disk is replaced by a new one the array is rebuilt while the system continues to operate normally. Some systems have to be shut down when removing or adding a drive; others support hot swapping, allowing drives to be replaced without powering down. RAID with hot-swap drives is often used in high availability systems, where it is important that the system keeps running as much of the time as possible.
It is important to note that redundant RAID is not an alternative to backing up data. Data may become damaged or destroyed without harm to the drive(s) on which it is stored. For example, part of the data may be overwritten by a system malfunction; a file may be damaged or deleted by user error or malice and not noticed for days or weeks; and of course the entire array is at risk of catastrophes such as theft, flood, and fire.
RAID principles
RAID combines two or more physical hard disks into a single logical unit by using either special hardware or software. Hardware solutions often are designed to present themselves to the attached system as a single hard drive, and the operating system is unaware of the technical workings. Software solutions are typically implemented in the operating system, and again would present the RAID drive as a single drive to applications.
There are three key concepts in RAID: mirroring, the copying of data to more than one disk; striping, the splitting of data across more than one disk; and error correction, where redundant data is stored to allow problems to be detected and possibly fixed (known as fault tolerance). Different RAID levels use one or more of these techniques, depending on the system requirements. The main aims of using RAID are to improve reliability, important for protecting information that is critical to a business, for example a database of customer orders; or where speed is important, for example a system that delivers video on demand TV programs to many viewers.
The configuration affects reliability and performance in different ways. The problem with using more disks is that it is more likely that one will go wrong, but by using error checking the total system can be made more reliable by being able to survive and repair the failure. Basic mirroring can speed up reading data as a system can read different data from both the disks, but it may be slow for writing if the configuration requires that both disks must confirm that the data is correctly written. Striping is often used for performance, where it allows sequences of data to be read from multiple disks at the same time. Error checking typically will slow the system down as data needs to be read from several places and compared. The design of RAID systems is therefore a compromise and understanding the requirements of a system is important. Modern disk arrays typically provide the facility to select the appropriate RAID configuration.
Standard levels
A number of standard schemes have evolved which are referred to as levels. There were five RAID levels originally conceived, but many more variations have evolved, notably several nested levels and many non-standard levels (mostly proprietary).
A brief summary of the most commonly used RAID levels. The SNIA Dictionary also contains definitions of the RAID levels that have been vetted by major storage industry players, and is referenced below as applicable. (RAID 2 is not included here as there are no commercial implementations of that level.)
| Level | Description | Minimum # of disks | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 0 | Striped set without parity/[Non-Redundant Array]. Provides improved performance and additional storage but no fault tolerance. Any disk failure destroys the array, which becomes more likely with more disks in the array. A single disk failure destroys the entire array because when data is written to a RAID 0 drive, the data is broken into fragments. The number of fragments is dictated by the number of disks in the drive. The fragments are written to their respective disks simultaneously on the same sector. This allows smaller sections of the entire chunk of data to be read off the drive in parallel, giving this type of arrangement huge bandwidth. RAID 0 does not implement error checking so any error is unrecoverable. More disks in the array means higher bandwidth, but greater risk of data loss. SNIA definition. | 2 | 
|
| RAID 1 | Mirrored set without parity. Provides fault tolerance from disk errors and single disk failure. Increased read performance occurs when using a multi-threaded operating system that supports split seeks, very small performance reduction when writing. Array continues to operate so long as at least one drive is functioning. SNIA definition. Using RAID 1 with a separate controller for each disk is sometimes called duplexing. | 2 | 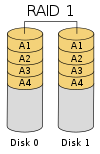
|
| RAID 2 | Redundancy through Hamming code.Disks are synchronised. It consist of very small stripes,often single byte /word. Error correction calculated across corresponding bits on disks. Multiple parity disks store Hamming code error correction in corresponding positions(for redundancy Hamming code is used). Since for redundancy, less disk units are used. SNIA definition | 3 | RAID Level 2 |
| RAID 3 | Striped set with dedicated parity/Bit interleaved parity. This mechanism provides an improved performance and fault tolerance similar to RAID 5, but with a dedicated parity disk rather than rotated parity stripes. The single parity disk is a bottle-neck for writing since every write requires updating the parity data. One minor benefit is the dedicated parity disk allows the parity drive to fail and operation will continue without parity or performance penalty. SNIA definition | 3 | 
|
| RAID 4 | Block level parity. Identical to RAID 3 but does block-level striping instead of byte-level striping. In this size of each stripe is large i.e. Block. Now a single file can be stored in a block, In this each disk operate independently and so many different I/O request can be satisfied in parallel. But data transfer speed for each I/O request will be less. The error detection is done by block level parity and is stored in separate single disk unit. SNIA definition | 3 | 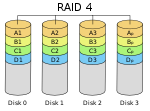
|
| RAID 5 | Striped set with distributed parity. Distributed parity requires all drives but one to be present to operate; drive failure requires replacement, but the array is not destroyed by a single drive failure. Upon drive failure, any subsequent reads can be calculated from the distributed parity such that the drive failure is masked from the end user. The array will have data loss in the event of a second drive failure and is vulnerable until the data that was on the failed drive is rebuilt onto a replacement drive. SNIA definition | 3 | 
|
| RAID 6 | Striped set with dual parity. Provides fault tolerance from two drive failures; array continues to operate with up to two failed drives. This makes larger RAID groups more practical, especially for high availability systems. This becomes increasingly important because large-capacity drives lengthen the time needed to recover from the failure of a single drive. Single parity RAID levels are vulnerable to data loss until the failed drive is rebuilt: the larger the drive, the longer the rebuild will take. Dual parity gives time to rebuild the array without the data being at risk if one drive, but no more, fails before the rebuild is complete. SNIA definition | 4 | 
|
Nested levels
Many storage controllers allow RAID levels to be nested: the elements of a RAID array may be either individual disks or RAIDs themselves. Nesting more than two deep is unusual.
As there is no basic RAID level numbered larger than 9, nested RAIDs are usually unambiguously described by concatenating the numbers indicating the RAID levels, sometimes with a "+" in between. For example, RAID 10 (or RAID 1+0) consists of several level 1 arrays of physical drives, each of which is one of the "drives" of a level 0 array striped over the level 1 arrays. RAID 0+1 is not called RAID 01 to avoid confusion with RAID 1. When the top array is a RAID 0 (such as in RAID 10 and RAID 50) most vendors omit the "+", though RAID 5+0 is clearer.
- RAID 0+1: striped sets in a mirrored set (minimum four disks; even number of disks) provides fault tolerance and improved performance but increases complexity. The key difference from RAID 1+0 is that RAID 0+1 creates a second striped set to mirror a primary striped set. The array continues to operate with one or more drives failed in the same mirror set, but if drives fail on both sides of the mirror the data on the RAID system is lost.
- RAID 1+0: mirrored sets in a striped set (minimum four disks; even number of disks) provides fault tolerance and improved performance but increases complexity. The key difference from RAID 0+1 is that RAID 1+0 creates a striped set from a series of mirrored drives. In a failed disk situation RAID 1+0 performs better because all the remaining disks continue to be used. The array can sustain multiple drive losses so long as no mirror loses both its drives.
- RAID 5+0: stripe across distributed parity RAID systems.
- RAID 5+1: mirror striped set with distributed parity (some manufacturers label this as RAID 53).
Non-standard levels
Many configurations other than the basic numbered RAID levels are possible, and many companies, organizations, and groups have created their own non-standard configurations, in many cases designed to meet the specialised needs of a small niche group. Most of these non-standard RAID levels are proprietary.
Some of the more prominent modifications are:
- CalDigit Inc HDPro adds parity RAID protection (RAID 5 and RAID 6) to subsystems which provides high-speed data transfer rate for 2K film, uncompressed high-definition video, standard-definition video, DVCProHD and HDV editing.
- ATTO Technology's DVRAID adds parity RAID protection to systems which demand performance for 4K film, 2K film, high-definition audio and video.
- Storage Computer Corporation uses RAID 7, which adds caching to RAID 3 and RAID 4 to improve I/O performance.
- EMC Corporation offered RAID S as an alternative to RAID 5 on their Symmetrix systems (which is no longer supported on the latest releases of Enginuity, the Symmetrix's operating system).
- The ZFS filesystem, available in Solaris, OpenSolaris, FreeBSD and Mac OS X, offers RAID-Z, which solves RAID 5's write hole problem.
- NetApp's Data ONTAP uses RAID-DP (also referred to as "double", "dual" or "diagonal" parity), which is a form of RAID 6, but unlike many RAID 6 implementations, does not use distributed parity as in RAID 5. Instead, two unique parity disks with separate parity calculations are used. This is a modification of RAID 4 with an extra parity disk.
- Accusys Triple Parity (RAID TP) implements three independent parities by extending RAID 6 algorithms on its FC-SATA and SCSI-SATA RAID controllers to tolerate three-disk failure.
- Linux MD RAID10 (RAID10) implements a general RAID driver that defaults to a standard RAID 1+0 with 4 drives, but can have any number of drives, including an odd number. MD RAID10 can run striped and mirrored with only 2 drives with the f2 layout (mirroring with striped reads, normal linux softraid 1 doesn't stripe reads, but can read in parallel) [1].
Implementations
The distribution of data across multiple drives can be managed either by dedicated hardware or by software. When done in software the software may be part of the operating system or it may be part of the firmware and drivers supplied with the card.
Operating system based ("software RAID")
Software implementations are now provided by many operating systems. A software layer sits above the (generally block-based) disk device drivers and provides an abstraction layer between the logical drives (RAIDs) and physical drives. Most common levels are RAID 0 (striping across multiple drives for increased space and performance) and RAID 1 (mirroring two drives), followed by RAID 1+0, RAID 0+1, and RAID 5 (data striping with parity) are supported.
Microsoft's server operating systems support 3 RAID levels; RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5. Microsoft desktop operating systems support RAID 0 only; there is no software support for fault-tolerant RAID levels in the desktop operating systems.
Apple's Mac OS X Server supports RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 1+0.[2]
The software must run on a host server attached to storage, and server's processor must dedicate processing time to run the RAID software. This is negligible for RAID 0 and RAID 1, but may be significant for more complex parity-based schemes. Furthermore all the busses between the processor and the disk controller must carry the extra data required by RAID which may cause congestion.
Another concern with operating system-based RAID is the boot process, it can be difficult or impossible to set up the boot process such that it can failover to another drive if the usual boot drive fails and therefore such systems can require manual intervention to make the machine bootable again after a failure. Finally operating system-based RAID usually uses formats specific to the operating system in question so it cannot generally be used for partitions that are shared between operating systems as part of a multi-boot setup.
Most operating system-based implementations allow RAIDs to be created from partitions rather than entire physical drives. For instance, an administrator could divide an odd number of disks into two partitions per disk, mirror partitions across disks and stripe a volume across the mirrored partitions to emulate a RAID 1E configuration. Using partitions in this way also allows mixing reliability levels on the same set of disks. For example, one could have a very robust RAID-1 partition for important files, and a less robust RAID-5 or RAID-0 partition for less important data. (Some high-end hardware controllers offer similar features, e.g. Intel Matrix RAID.) Using two partitions on the same drive in the same RAID is, however, dangerous. If, for example, a RAID 5 array is composed of four drives 250 + 250 + 250 + 500 GB, with the 500-GB drive split into two 250 GB partitions, a failure of this drive will remove two partitions from the array, causing all of the data held on it to be lost.
Hardware-based
Hardware RAID controllers use different, proprietary disk layouts, so it is not usually possible to span controllers from different manufacturers. They do not require processor resources, the BIOS can boot from them, and tighter integration with the device driver may offer better error handling.
A hardware implementation of RAID requires at least a special-purpose RAID controller. On a desktop system this may be a PCI expansion card, PCI-Express Expansion Card or built into the motherboard. Controllers supporting most types of drive may be used - IDE/ATA, SATA, SCSI, SSA, Fibre Channel, sometimes even a combination. The controller and disks may be in a stand-alone disk enclosure, rather than inside a computer. The enclosure may be directly attached to a computer, or connected via SAN. The controller hardware handles the management of the drives, and performs any parity calculations required by the chosen RAID level.
Most hardware implementations provide a read/write cache which, depending on the I/O workload, will improve performance. In most systems write cache may be non-volatile (e.g. battery-protected), so pending writes are not lost on a power failure.
Hardware implementations provide guaranteed performance, add no overhead to the local CPU complex and can support many operating systems, as the controller simply presents a logical disk to the operating system.
Hardware implementations also typically support hot swapping, allowing failed drives to be replaced while the system is running.
Firmware/driver based RAID ("fake RAID")
Operating system-based RAID cannot easily be used to protect the boot process and is generally impractical on desktop version of Windows (as described above). Hardware RAID controllers are expensive. To fill this gap cheap "RAID controllers" were introduced that do not contain a RAID controller chip, but simply a standard disk controller chip with special firmware and drivers. During early stage bootup the RAID is implemented by the firmware; when a protected-mode operating system such as a modern version of GNU/Linux or Microsoft Windows is loaded the drivers take over.
These controllers are described by their manufacturers as RAID controllers, and it is rarely made clear to purchasers that the burden of RAID processing is borne by the host computer's central processing unit, not the RAID controller itself, thus introducing the afore-mentioned CPU overhead. Before their introduction, a "RAID controller" implied that the controller did the processing, and the new type has become known in technically knowledgeable circles as "fake RAID" even though the RAID itself is implemented correctly.
Network-Attached Storage
While not directly associated with RAID, Network-Attached Storage (NAS) is an enclosure containing disk drives and the equipment necessary to make them available over a computer network, usually Ethernet. The enclosure is basically a dedicated computer in its own right, designed to operate over the network without screen or keyboard. It contains one or more disk drives; multiple drives may be configured as a RAID.
Hot spares
Both hardware and software RAIDs with redundancy may support the use of hot spare drives, a drive physically installed in the array which is inactive until an active drive fails, when the system automatically replaces the failed drive with the spare, rebuilding the array with the spare drive included. This reduces the mean time to repair (MTTR), though it doesn't eliminate it completely. A second drive failure in the same RAID redundancy group before the array is fully rebuilt will result in loss of the data; rebuilding can take several hours, especially on busy systems.
Rapid replacement of failed drives is important as the drives of an array will all have had the same amount of use, and may tend to fail at about the same time rather than randomly. RAID 6 without a spare uses the same number of drives as RAID 5 with a hot spare and protects data against simultaneous failure of up to two drives, but requires a more advanced RAID controller.
Reliability terms
- Failure rate
- The mean time to failure (MTTF) or the mean time between failure (MTBF) of a given RAID is the same as those of its constituent hard drives, regardless of what type of RAID is employed.
- Mean time to data loss (MTTDL)
- In this context, the average time before a loss of data in a given array.[3]. Mean time to data loss of a given RAID should be higher, but can be lower than that of its constituent hard drives, depending upon what type of RAID is employed.
- Mean time to recovery (MTTR)
- In arrays that include redundancy for reliability, this is the time following a failure to restore an array to its normal failure-tolerant mode of operation. This includes time to replace a failed disk mechanism as well as time to re-build the array (i.e. to replicate data for redundancy).
- Unrecoverable bit error rate (UBE)
- This is the rate at which a disk drive will be unable to recover data after application of cyclic redundancy check (CRC) codes and multiple retries.
- Write cache reliability
- Some RAID systems use RAM write cache to increase performance. Failure of the RAM can lose data.
- Atomic write failure
- Also known by various terms such as torn writes, torn pages, incomplete writes, interrupted writes, non-transactional, etc.
Issues with RAID
The theory behind the error correction in RAID assumes that failures of drives are independent. Given these assumptions it is possible to calculate how often they can fail and to arrange the array to make data loss arbitrarily improbable.
In practice, the drives are often the same ages, with similar wear. Since many drive failures are due to mechanical issues which are more likely on older drives, this violates those assumptions and failures are in fact statistically correlated. In practice then, the chances of a second failure before the first has been recovered is not nearly as unlikely as might be supposed, and data loss can in practice occur at significant rates.[4]
Atomicity
This is a little understood and rarely mentioned failure mode for redundant storage systems that do not utilize transactional features. Database researcher Jim Gray wrote "Update in Place is a Poison Apple" [5]during the early days of relational database commercialization. However, this warning largely went unheeded and fell by the wayside upon the advent of RAID, which many software engineers mistook as solving all data storage integrity and reliability problems. Many software programs update a storage object "in-place"; that is, they write a new version of the object on to the same disk addresses as the old version of the object. While the software may also log some delta information elsewhere, it expects the storage to present "atomic write semantics," meaning that the write of the data either occurred in its entirety or did not occur at all.
However, very few storage systems provide support for atomic writes, and even fewer specify their rate of failure in providing this semantic. Note that during the act of writing an object, a RAID storage device will usually be writing all redundant copies of the object in parallel, although overlapped or staggered writes are more common when a single RAID processor is responsible for multiple drives. Hence an error that occurs during the process of writing may leave the redundant copies in different states, and furthermore may leave the copies in neither the old nor the new state. The little known failure mode is that delta logging relies on the original data being either in the old or the new state so as to enable backing out the logical change, yet few storage systems provide an atomic write semantic on a RAID disk.
While the battery-backed write cache may partially solve the problem, it is applicable only to a power failure scenario.
Since transactional support is not universally present in hardware RAID, many operating systems include transactional support to protect against data loss during an interrupted write. Novell Netware, starting with version 3.x, included a transaction tracking system. Microsoft introduced transaction tracking via the journalling feature in NTFS. NetApp WAFL file system solves it by never updating the data in place, as does ZFS.
Unrecoverable data
This can present as a sector read failure. Some RAID implementations protect against this failure mode by remapping the bad sector, using the redundant data to retrieve a good copy of the data, and rewriting that good data to the newly mapped replacement sector. The UBE rate is typically specified at 1 bit in 1015 for enterprise class disk drives (SCSI, FC, SAS) , and 1 bit in 1014 for desktop class disk drives (IDE, ATA, SATA). Increasing disk capacities and large RAID 5 redundancy groups have led to an increasing inability to successfully rebuild a RAID group after a disk failure because an unrecoverable sector is found on the remaining drives. Double protection schemes such as RAID 6 are attempting to address this issue, but suffer from a very high write penalty.
Write cache reliability
The disk system can acknowledge the write operation as soon as the data is in the cache, not waiting for the data to be physically written. However, any power outage can then mean a significant data loss of any data queued in such cache.
Often a battery is protecting the write cache, mostly solving the problem. If a write fails because of power failure, the controller may complete the pending writes as soon as restarted. This solution still has potential failure cases: the battery may have worn out, the power may be off for too long, the disks could be moved to another controller, the controller itself could fail. Some disk systems provide the capability of testing the battery periodically, which however leaves the system without a fully charged battery for several hours.
Equipment compatibility
The disk formats on different RAID controllers are not necessarily compatible, so that it may not be possible to read a RAID on different hardware. Consequently a non-disk hardware failure may require using identical hardware, or a data backup, to recover the data.
History
Norman Ken Ouchi at IBM was awarded a 1978 U.S. patent 4,092,732[6] titled "System for recovering data stored in failed memory unit." The claims for this patent describe what would later be termed RAID 5 with full stripe writes. This 1978 patent also mentions that disk mirroring or duplexing (what would later be termed RAID 1) and protection with dedicated parity (that would later be termed RAID 4) were prior art at that time.
The term RAID was first defined by David A. Patterson, Garth A. Gibson and Randy Katz at the University of California, Berkeley in 1987. They studied the possibility of using two or more drives to appear as a single device to the host system and published a paper: "A Case for Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID)" in June 1988 at the SIGMOD conference.[7]
This specification suggested a number of prototype RAID levels, or combinations of drives. Each had theoretical advantages and disadvantages. Over the years, different implementations of the RAID concept have appeared. Most differ substantially from the original idealized RAID levels, but the numbered names have remained. This can be confusing, since one implementation of RAID 5, for example, can differ substantially from another. RAID 3 and RAID 4 are often confused and even used interchangeably.
Their paper formally defined RAID levels 1 through 5 in sections 7 to 11:
- First level RAID: mirrored drives
- Second level RAID: Hamming code for error correction
- Third level RAID: single check disk per group
- Fourth level RAID: independent reads and writes
- Fifth level RAID: spread data/parity over all drives (no single check disk)
See also
- Disk Data Format (DDF)
- Redundant Arrays of Hybrid Disks (RAHD)
- Redundant Array of Independent Filesystems
- Redundant Array of Inexpensive Nodes
- Redundant Array of Inexpensive Servers
- Vinum volume manager
References
- ^ Main Page - Linux-raid
- ^ "Apple Mac OS X Server File Systems". Retrieved 2008-04-23.
- ^ Jim Gray and Catharine van Ingen, "Empirical Measurements of Disk Failure Rates and Error Rates", MSTR-2005-166, December 2005
- ^ Disk Failures in the Real World: What Does an MTTF of 1,000,000 Hours Mean to You? Bianca Schroeder and Garth A. Gibson
- ^ Jim Gray: The Transaction Concept: Virtues and Limitations (Invited Paper) VLDB 1981: 144-154
- ^ U.S. patent 4,092,732
- ^
Patterson, David (1988). "A Case for Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID)" (PDF). SIGMOD Conference. pp. pp 109–116.
{{cite conference}}:|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) retrieved 2006-12-31
Further reading
- Charles M. Kozierok (2001-04-17). "Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks". The PC Guide. Pair Networks.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
External links
- Tutorial on "RAID 6 Essentials"
- RAID Disk Space Calculator
- Working RAID illustrations
- RAID Levels — Tutorial and Diagrams
- Slashdot: Which RAID for a Personal Fileserver? — Comments from network specialists and enthusiasts.
- Logical Volume Manager Performance Measurement
- Animations and Descriptions to help Learn about RAID Levels 0, 1, 5, 10, and 50
- RAID Calculator
- RAID Controller (German)
White papers
There has been a significant amount of research done into the technical aspects of this storage method. Technical institutions and involved companies have released white papers and technical documentation relevant to RAIDs and made them available to the public. They are accessible below
- Tutorial on Reed-Solomon Coding for Fault-Tolerance in RAID-like Systems
- Parity Declustering for Continuous Operation in Redundant Disk Arrays
- An Optimal Scheme for Tolerating Double Disk Failures in RAID Architectures
Operating system-specific details
If you would like more information detailing the deployment, maintenance, and repair of RAIDs on a specific operating system, the external links below, sorted by operating system, could prove useful.
- IBM - seriesI/iSeries/AS400 Running OS400/i5OS
- Novell
- Linux
- Linux Software-RAID HOWTO
- RAID-1 QUICK Howto under Linux (Note: Site appears to be down as of 5/21/2007).
- Experiences w/ Software RAID 5 Under Linux? — "Ask Slashdot" article on RAID 5.
- Optimal Hardware RAID Configuration for Linux. Make it up to 30% faster by aligning the file system to the RAID stripe structure.
- Growing a RAID 5 array Blog post which describes using mdadm to grow a RAID 5 array to include more disk space.
- Linux Software Raid 1 Setup
- Microsoft Windows
- Basic Storage Versus Dynamic Storage in Windows XP RAID functionality built into Windows 2000/XP
- Windows Software RAID Guide
- Microsoft Best Practices Guide
