Estrogen receptor
| Estrogen receptor, α subunit | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 595 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer, heterodimer | |
| Isoforms | Long, short | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | ESR1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | multicellular animals | |
| Estrogen receptor, β subunit | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 530 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer, heterodimer | |
| Isoforms | 8th | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | ESR2 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Mammals | |
Estrogen receptors (ER), also called estrogen receptors , are steroid receptors that belong to the superfamily of nuclear receptors NR3I ( nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group I ) and are activated by the steroid hormone estrogen . The most important function of the estrogen receptor is a DNA- binding transcription factor , which regulates the gene expression of the target gene . The estrogen receptor, however, has additional functions independent of the DNA binding.
Structure and bond
Two human receptor subtypes could be identified, both of which have the same basic structure:
- Estrogen receptor-α (ERα, NR3A1)
- Estrogen receptor-β (ERβ, NR3A2)
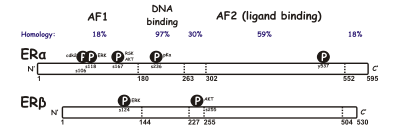
Both receptors have six domains (A – F):
- A / B domain: Contains a ligand-independent transcriptional activation function (AF-1).
- C domain: DNA binding domain (DBD). It contains two zinc finger motifs .
- D domain: dimerization region.
- E / F domain: Contains the ligand binding domain (LBD) and a so-called transactivation region at the C terminus (AF-2).
Since both subtypes are expressed simultaneously in many cells, the hormone-activated receptor dimerization leads to the formation of ERα (αα) or ERβ (ββ) homodimers or ERαβ (αβ) heterodimers.
Different ligands can differ in their affinity for the two receptor isoforms:
- Estradiol and Coumestrol bind to both receptors
- Estrone and raloxifene bind preferentially to ERα
- Estriol and genistein bind to ERβ
Selective estrogen receptor modulators preferentially bind to either the α or β subtype of the receptor.
The survival rate of breast cancer patients correlates more strongly with the results of the immunohistochemical staining of the estrogen receptor than with the detection of the mRNA of the estrogen receptor. Groups of patients with tumors that have the estrogen receptor β but not the estrogen receptor α have higher survival rates.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Dahlman-Wright, K. et al. (2006): International Union of Pharmacology. LXIV. Estrogen receptors. In: Pharmacol Rev . 58 (4): 773-781. PMID 17132854 PDF
- ^ Levin, ER (2005): Integration of the extranuclear and nuclear actions of estrogen. In: Mol Endocrinol . 19 (8): 1951-1959. PMID 15705661 doi : 10.1210 / me.2004-0390
- ↑ Morito K, Aomori T, Hirose T, et al : Interaction of phytoestrogens with estrogen receptors alpha and beta (II) . In: Biol Pharm Bull . 25, No. 1, January 2002, pp. 48-52. PMID 11824555 .
- ^ A b W. Tan, Q. Li, K. Chen, F. Su, E. Song, C. Gong: Estrogen receptor beta as a prognostic factor in breast cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. In: Oncotarget. [Electronic publication before going to press] February 2016, doi : 10.18632 / oncotarget.7219 , PMID 26863572 .
Web links
- Jennifer McDowall / Interpro: Protein Of The Month: Oestrogen receptors. (engl.)
- Orphanet: Estrogen resistance syndrome.