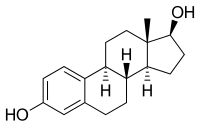
Estradiol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Estradiol | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 24 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless prisms |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 272,39 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
177 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
readily soluble in many organic solvents, hardly soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Estradiol or estradiol , sometimes abbreviated as E 2 , is a sex hormone and, in comparison with estrone and estriol, the most effective natural estrogen (estrogen). It is mainly produced in the follicles of the ovaries .
properties
In women, most of the estradiol is produced by granulosa cells in the ovaries . The precursor estrone is formed in the theca folliculi cells via the intermediate stage androstenedione . In addition, estradiol is formed in the placenta (during pregnancy) and, to a lesser extent, in the adrenal cortex and - in men - in the testicles . In fat cells can testosterone is converted to estradiol. Estradiol is also made in the brain and in arteries . Estradiol is also found in men as an active metabolic product of testosterone. The serum level of estradiol in men is between 14 and 55 pg / mL and is comparable to that of a woman during menopause (<35 pg / mL).
In vivo , estradiol is interchangeable with estrone; the conversion of estradiol into estrone is possible. Estradiol not only has a major influence on sexual and reproductive function, but also has an effect on other organs, such as the bones.
Estradiol has two hydroxyl groups in its molecular structure and is therefore referred to as E 2 , while estrone with only one hydroxyl group as E 1 and estriol with three as E 3 . Estradiol is about ten times more potent than estrone and about 80 times more potent than estriol in terms of its estrogenic effects. Except during the early proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle , its serum level is slightly higher than that of estrone during a woman's reproductive years; therefore, estradiol is the predominant estrogen during the reproductive years in terms of absolute serum levels and estrogenic activity. The predominant circulating estrogen in the body is estrone during menopause, whereas it is estriol during pregnancy.
effect
Estrogens promote the growth of the vagina (sheath), uterus , ovaries and fallopian tubes as well as the development of secondary female sexual characteristics.
As part of the menstrual cycle , estrogens have a strong influence on the uterus. In the early stages of the menstrual cycle, they stimulate the endometrium to grow, muscle fibers increase in number and size, and blood flow is stimulated. Furthermore, the cervical mucus becomes spinnable. The cyclical influence of estrogens on the epithelium of the vagina could also be demonstrated. However, estrogens have an adverse effect on cartilage formation, in contrast to their hormonal counterpart, testosterone . The estradiol concentration during menstruation is <50 pg / ml. With the formation of the ovarian follicle , it reaches a peak of 200 pg / ml, decreases briefly during ovulation and increases briefly in the corpus luteum phase , and then drops to the normal level if there is no pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the blood level increases of estrogens to birth at 10 to 100 times more, then on the eighth day after fertilization in the placenta (placenta) chorionic gonadotropin is produced (hCG) that the transformation of the corpus luteum in the corpus luteum gravitatis causes. Corpus luteum gravitatis and placenta ensure high levels of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy . This prevents menstruation and promotes the growth of the uterus and fruit.
According to a study that has not yet been reproduced, there is a correlation between higher estradiol values, as well as the attractiveness assessed by oneself and others, and the inclination to sex outside a fixed relationship.
Estradiol has an increasing influence on bone density . The likelihood of breast and ovarian cancer increases with the concentration of estradiol. In men, an increased estrogen level can lead to feminization .
biochemistry
In the organism , cholesterol is the starting material for estradiol synthesis. Via pregnenolone , progesterone , 17 α -hydroxyprogesterone , androst-4-en-3,17-dione , testosterone and 19-hydroxytestosterone , an aromatase ultimately produces estradiol. It can be converted into estrone by oxidation of the OH group in position 17 . Estradiol is broken down by 4-hydroxylation using CYP1B1 .
Steroid hormones can freely diffuse through cell membranes as lipids in the body and activate gene expression by binding to the receptor, which is usually also a transcription factor . Unlike many other hormones (such as adrenaline ), steroid hormones have to penetrate the target cell. In the cytosol of the cell, the hormone binds to its hormone receptor (in this case to an estrogen receptor ). The complex of hormone and receptor is transported into the cell nucleus. There the transcription of mRNA of certain genes is initiated. This is the first step in protein synthesis. This hormone reaches its full effect only after hours, not within minutes, because its biological effect depends on the synthesis of these new proteins.
Most of the estradiol in the serum is complexed with the sex hormone-binding globulin and albumin . About 2.21% of estradiol is biologically active. A part is absorbed via the enterohepatic circulation . Estradiol is metabolized by glucuronidation and sulfation in the liver and excreted in the urine .
Derivatives of estradiol
- Ethinylestradiol , often the estrogenic component in combination products of the birth control pill
- Mestranol , a prodrug (an inactive precursor) of ethinylestradiol
Trade names
Climara (CH), Dermestril (D), Divigel (CH), Estraderm (D), Estradot (D, A, CH), Estramon (D, A, CH), Estreva (D), Estrifam (D), Estring ( D, CH), Estrofem (CH), Estronorm (D), Fem7 (D), Femoston mono (D, CH), Gynokadin (D), GynPolar (D), Klimapur (A), Oestrogel (CH), Sandrena ( CH), Systen (CH), Vagifem (CH), Generika (D), Linoladiol N Creme (D)
Activelle (D, A, CH), Angeliq (D, A, CH), Climen (CH), Clionara (D), Cutanum (D), Estalis (D, A, CH), Estragest (D, CH), Fem7 Combi (D), Femoston (D, A, CH), Gynamon (D), Gynodian (CH), Indivina (CH), Kliogest (D, A, CH), Merigest (CH), Novofem (D, CH), Osmil (D), Sequidot (D), Triaval (CH), Tri-sequence (A, CH)
literature
- Lois Jovanovic, Genell J. Subak-Sharpe: Hormones. The medical manual for women. (Original edition: Hormones. The Woman's Answerbook. Atheneum, New York 1987) From the American by Margaret Auer, Kabel, Hamburg 1989, ISBN 3-8225-0100-X , pp. 34 and 382.
Web links
- Jassal / reactome: Testosterone is converted to estradiol
- Jassal / reactome: CYP1B1 4-hydroxylates estradiol-17beta
- Explanation and illustrations by Wolfgang Hübl (specialist in medical and chemical laboratory diagnostics)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on estradiol. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 9, 2014.
- ↑ P. Velluz: Bull. Soc. Chim. France 1948 , 1113.
- ↑ a b data sheet β-estradiol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 31, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Entry on estradiol in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ Kristina M. Durante, Norman P. Li: Oestradiol level and opportunistic mating in women . In: Biology Letters . tape 5 , no. 2 , April 23, 2009, ISSN 1744-9561 , p. 179-182 , doi : 10.1098 / rsbl.2008.0709 , PMID 19141415 ( royalsocietypublishing.org [accessed August 16, 2017]).
- ^ CH Wu, T. Motohashi, HA Abdel-Rahman, GL Flickinger, G. Mikhail: Free and protein-bound plasma estradiol-17β during the menstrual cycle . In: J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. . 43, No. 2, August 1976, pp. 436-445. doi : 10.1210 / jcem-43-2-436 . PMID 950372 .

