Human chorionic gonadotropin
| Human chorionic gonadotropin, β subunit | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
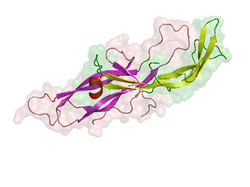
| Structural model according to PDB 1HRP | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 145 amino acids | |
| Isoforms | SNPs | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | CGB ; CGB3 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Drug information | ||
| ATC code | G03 GA08 | |
| DrugBank | DB00097 | |
| Drug class | hormone | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | LH-beta | |
| Parent taxon | Vertebrates | |
The human chorionic gonadotropin , shortly hCG is a peptide hormone (specifically, a gonadotropin ), which during pregnancy by human syncytiotrophoblast (part of the placenta is formed), is responsible for starting and maintaining pregnancy and can therefore laboratory tests used for early pregnancy determination. Chorionic gonadotropin as a hormone produced by the cells of the placenta is not unique to humans.
structure
Human chorionic gonadotropin is a glycoprotein and consists of two subunits, the α-subunit ( α-hCG ) with 92 amino acids and the β-subunit (β-hCG) with 145 amino acids. The β subunit is specific for the hCG. The α subunit, on the other hand, is also found in other hormones: follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH) and thyrotropin (TSH).
concentration
In men and non-pregnant women, the normal value of the hCG concentration in the blood is up to 5 IU / liter. In women, after the onset of menopause, the normal value increases to up to 10 IU / liter. The concentration increases about five days after implantation. In the third week after conception the values are still below 50 IU / liter, in the fourth week below 400 IU / liter. The maximum is reached in the 10th to 12th week with up to 230,000 IU / liter. The concentration then drops again and is between 5,000 and 65,000 IU / liter towards the end of pregnancy. Other studies describe maximum values of 289,000 IU / liter and report values between 940 and 60,000 IU / liter towards the end of pregnancy. Normal values are reached again around 11 to 17 days after the birth.
The concentration in the urine is lower in each case. Over-the-counter pregnancy tests usually show a positive result from 25 IU / liter in the urine.
function
At the beginning of pregnancy , approx. 114 hours (middle of the fifth day) after fertilization, a special form of hCG, the hyperglycosylated hCG, begins to prepare the nidation of the blastocyst . For this purpose, some cells of the blastocyst differentiate into mononuclear cytotrophoblast cells, in which the hyperglycosylated hCG is initially predominantly formed. Through contact with the endometrium (the mucous membrane) of the uterus, some trophoblast cells differentiate and proliferate into polynuclear syncytiotrophoblasts, in which the biologically active hCG is subsequently produced. The primary chorion with its villi emerges from these two cell forms , the early form of the child's part of the placenta . HCG stimulates the corpus luteum ( the corpus luteum ) in ovarian for distribution of another hormone, progesterone , which constitutes the uterine mucosa and signals the ovaries via negative feedback to the pituitary gland, that for the time being no ovulations are necessary (more ovulations remain off). Since the corpus luteum does not perish during pregnancy, but rather maintains the release of progesterone, there is no menstrual bleeding and the uterine lining that has built up before ovulation is loosened. The corpus luteum does not degenerate into a scarred corpus albicans ; it develops into a corpus luteum graviditatis .
In the first few weeks of pregnancy, the hCG concentration in the blood rises steadily, the hormone levels double approximately every two days. The maximum is reached between the eighth and tenth week of pregnancy. Thereafter, the hCG values slowly drop to basal concentrations that are reached shortly before the 20th week of pregnancy. Until the placenta is mature enough to produce the pregnancy-maintaining hormone progesterone itself, the corpus luteum can continue to produce progesterone until the end of the 4th month of pregnancy.
proof
Detection of significant amounts of human chorionic gonadotropin in a woman's blood or urine is a very important sign of pregnancy . Almost all pregnancy tests work by detecting the β-hCG subunit specific for the hCG. This is done immunologically by antibodies against epitopes of the β subunit. Depending on the binding sites on the hCG hormone, such immunological assays only measure the complete dimeric hormone (intact hCG) or the complete hormone plus free β chain (total hCG), which is often erroneously referred to as "β-hCG". Less than 1% of total hCG is free, i.e. H. unbound β-hCG, which is why it does not make sense to use tests that can only react with this small subset to determine pregnancy.
However, the determination of the free β-hCG is important in the search for chromosomal disorders, especially trisomy 21 , in the first trimester of pregnancy ( first trimester screening ).
Tumor markers
Human chorionic gonadotropin is also of some tumors of the gonads or the placenta - such as non-seminomas , seminoma , choriocarcinoma and ovarian cancer produces. Increased hCG levels are less common in tumors of the breast , liver , small intestine , colon and kidneys, as well as in bronchial carcinoma . Because of its low specificity, the value is not suitable for diagnosing a tumor disease. Like almost every tumor marker, it can only be used to assess the course of a known disease. In addition, an increased hCG concentration can be an indication of a multiple pregnancy , a mole of bladder or a fetal trisomy 21 ( Down's syndrome ).
Further application
The property of hCG to stimulate the body's own testosterone production can be used to counteract testicular atrophy in men. Weightlifting or bodybuilding athletes who use anabolic steroids such as Dianabol and Sustanon to improve their performance inject hCG to prevent the testicular shrinkage caused by the use of artificial testosterone. In medicine, hCG is used in the treatment of non-descended testes ( cryptorchidism ) in boys as well as to improve fertility in women.
hCG antibodies
Since the hCG exerts an immune tolerance both in pregnancy and in tumors, there are studies with an hCG vaccination consisting of hCG and diphtheria toxoids. As a result, the body produces antibodies against hCG, which can be used to combat tumors on the one hand and for contraception on the other (cf. also w: en: AVICINE ). A first field test was carried out as early as 1993/1994, whereby the women, who had all already been sterilized, were informed beforehand about the suspected effects. This study is being used by vaccination opponents as "evidence" for their claims that tetanus vaccination campaigns are secretly sterilizing women. The Kenyan Conference of Catholic Bishops also made this accusation in January 2015, following relevant investigations .
hCG diet
British endocrinologist Albert TW Simeons first recommended hCG as an addition to an ultra-low calorie weight loss diet (less than 500 calories). Simeons studied pregnant women in India who were on a low-calorie diet . On treatment with small doses of hCG, Simeons found that his patients were more likely to lose fat than muscle tissue .
In 1954, Simeons published his book Pound and Inches on weight loss . As a practicing physician at the Salvator Mundi Hospital in Rome, he recommended small daily hCG injections to patients, combined with an individual ultra-low-calorie, high-protein, low-carbohydrate and low-fat diet . The goal of this diet was to lose fat tissue without losing muscle tissue.
Simeon's research results were never taken up or expanded by other researchers. In response to complaints in 1976, the American Food and Drug Administration ordered that all advertisements for hCG diets should include the following notice:
"These weight reduction treatments include the injection of HCG, a drug which has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration as safe and effective in the treatment of obesity or weight control. There is no substantial evidence that HCG increases weight loss beyond that resulting from caloric restriction, that it causes a more attractive or normal distribution of fat, or that it decreases the hunger and discomfort associated with calorie-restrictive diets. "
There was a resurgence of interest in hCG diets after Kevin Trudeau began promoting it. He later received a ban from the Federal Trade Commission to make further claims regarding hCG diets. The ban ultimately resulted in Kevin Trudeau being sentenced to prison.
The general scientific consensus is that any weight loss reported by participants on the hCG diet is entirely due to a daily intake of just 500–1000 calories, well below the recommended amount for adults.
swell
- ↑ UniProt P01233
- ↑ Thomas L., Labor und Diagnose, 5th edition, 2000.
- ↑ Cacciatore B. et al., Brit J Obstetr Gynaecol 1990; 97: 899-903.
- ↑ Braunstein GD., HCG Testing: Volume II. Answers to Frequently Asked Questions about hCG Testing. Monograph, 97-9325, 1991. Abbott Diagnostics. Educational Services. Abbott Park, IL.
- ↑ babyhopes.com
- ↑ Talwar GP, Singh O, Pal R, ua: A vaccine that prevents pregnancy in women . In: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA . 91, No. 18, August 1994, pp. 8532-6. PMID 8078917 . PMC 44640 (free full text).
- ↑ Are New Vaccines Laced with Birth-Control Drugs? by James A. Miller, special correspondent for Human Life International . This article was originally published in HLI Reports, Human Life International , Gaithersburg, Maryland; June / July 1995, Volume 13, Number 8. Retrieved June 22, 2010
- ↑ KENYA CONFERENCE OF CATHOLIC BISHOPS - STATEMENT BY THE KENYA CONFERENCE OF CATHOLIC BISHOPS ON MASS TETANUS VACCINATION CAMPAIGN CARRIED OUT IN KENYA IN MARCH AND OCTOBER 2014. Accessed March 31, 2020 (American English).
- ↑ a b Simeon's ATW: Pounds & Inches: A New Approach To Obesity . Popular Publishing, 2010, ISBN 0-615-42755-3 .
- ^ In the Matter of Simeon Management Corp. (Fed. Trade Comm'n, 1976) 87 FTC 1184; affirmed by Simeon Management Corp. v. FTC (9th Cir. 1978) 579 F.2d 1137, 49 ALR-Fed 1.
- ↑ Kevin Trudeau Banned from Infomercials For Three Years, Ordered to Pay More Than $ 5 Million for False Claims About Weight-Loss Book ; FTC v. Trudeau (7th Cir., 2009) 579 F.3d 754 remanded (NDIll., 2010) 708 F.Supp.2d 711, affirmed (7th Cir. 2011) 662 F.3d 947, certiorari denied (Oct. 9, 2012) _U.S._, 133 S.Ct. 426, 184 L.Ed.2d 257; and a ten-year prison sentence for violating a court order, US v. Trudeau (NDIll., Jan. 29, 2014) 2014 usdist. LEXIS 10717, 2014 WL 321373. And the article, The Curious Case of Kevin Trudeau, King Catch Me If You Can by Catherine Bryant Bell, Mississippi Law Journal, vol. 79 page 1043 (summer 2010), http://heinonline.org/HOL/Page?handle=hein.journals/mislj79&div=44&g_sent=1&collection=journals#1053 .
- ↑ Does the HCG diet work - and is it safe? , Mayo Clinic
See also
Web links
- Synthesis and Degradation of hCG ( Memento from January 16, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- Laboratory results: hCG