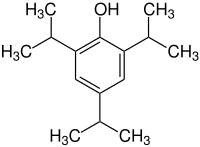
2,4,6-triisopropylphenol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,4,6-triisopropylphenol | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 24 O | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 220.35 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
2,4,6-triisopropylphenol is an aromatic compound . It is a derivative of phenol with three isopropyl groups .
It is obtained by triple Friedel-Crafts alkylation of phenol with propylene at about 150.degree.
It is used as an intermediate in the production of other chemical compounds; for example derived phosphates, which serve as plasticizers in PVC.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b Patent US4275248 : Preparation of 2,4,6-triisopropylphenol. Applied on April 9, 1980 , published June 23, 1981 , applicant: UOP Inc. , inventor: Bruce E. Firth.
- ↑ YES Brydson: Plastics Materials . Butterworth-Heinemann, 1999, ISBN 978-0-08-051408-6 , pp. 333 ( limited preview in Google Book search).