Fluorobenzaldehyde
| Fluorobenzaldehyde | |||||
| Surname | 2-fluorobenzaldehyde | 3-fluorobenzaldehyde | 4-fluorobenzaldehyde | ||
| other names | o -fluorobenzaldehyde | m -fluorobenzaldehyde | p -fluorobenzaldehyde | ||
| Structural formula |

|
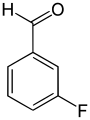
|

|
||
| CAS number | 446-52-6 | 456-48-4 | 459-57-4 | ||
| PubChem | 67970 | 68009 | 68023 | ||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 FO | ||||
| Molar mass | 124.12 g mol −1 | ||||
| Physical state | liquid | ||||
| Melting point | −44.5 ° C | −10 ° C | |||
| boiling point | 172-174 ° C | 169-174 ° C | 176-179 ° C | ||
|
GHS labeling |
|
||||
| H and P phrases | 226-315-319-335 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | |||||
| 261-305 + 351 + 338 | |||||
In chemistry, fluorobenzaldehydes are a group of substances that are derived from both benzaldehyde and fluorobenzene . The structure consists of a benzene ring with an attached aldehyde group (–CHO) and fluorine (–F) as substituents . Their different arrangements ( ortho , meta or para ) result in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 7 H 5 FO.
properties
The introduction of the fluorine atom changes the boiling point only slightly compared to benzaldehyde (179 ° C).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b data sheet 2-fluorobenzaldehydes from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 29, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Data sheet 4-Fluorobenzaldehyde from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 29, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c FLUKA catalog 2001/2002, p. 656.
- ↑ Data sheet 3-Fluorobenzaldehyde from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 3, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on benzaldehyde in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 27, 2014(JavaScript required) .

