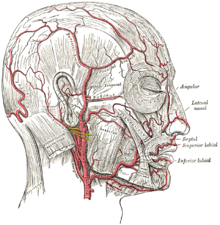
Superficial temporal artery
The superficial temporal artery ("superficial temporal artery") is the last branch of the external carotid artery ( external carotid artery ), which is subsequently referred to as the maxillary artery ("maxillary artery"). The superficial temporal artery runs in front of the ear over the temple and supplies the upper half of the head. The pulse can be felt on the artery just in front of the ear above the zygomatic arch . The artery is accompanied by the auriculotemporal nerve and the vein of the same name ( vena temporalis superficialis ).
Inflammation of the temporal artery ( giant cell arteritis ) is most common in older people.
branch
The superficial temporal artery discharges several branches:
- The arteria transversa faciei ("transverse facial artery") runs below the zygomatic arch and supplies the parotid gland , the masseter muscle and the skin of the face.
- The arteria temporalis media ("middle temporal artery") originates above the zygomatic arch and supplies the musculus temporalis .
- The ramus zygomaticoorbitalis ("zygomatic orbital branch") sometimes arises from the arteria temporalis media and extends into the eye area, where it also supplies the orbicularis oculi muscle and the eyelids.
- The rami auriculares anteriores ("front ear branches") supply the front part of the auricle and the external auditory canal .
- The Ramus frontalis ("forehead branch") is one of the two end branches and extends into the forehead region .
- The ramus parietalis ("vertex load") pulls into the vertex area .
literature
- Uwe Gille: Cardiovascular and immune system, Angiologia. In: Franz-Viktor Salomon, Hans Geyer, Uwe Gille (Ed.): Anatomy for veterinary medicine. 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Enke, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8304-1075-1 , pp. 404-463.