Alizarin dyes
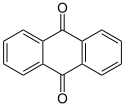
The alizarin dyes are a group of important, mainly synthetic mordant dyes (see development color ). Because of the anthraquinone structure, they are classified as anthraquinone dyes . In addition to alizarin, purpurin also occurs naturally.
history
The German chemist Robert Emanuel Schmidt conducted research at the Friedrich Bayer paint factory from 1887 and developed the first synthetic alizarin dye in 1889.
Derivatives
The alizarin dyes are derivatives of alizarin - an anthraquinone substituted with two phenolic hydroxyl groups - which differ in terms of different substituents on the two outer benzene rings.
| Surname | structure | R 1 | R 2 | R 3 | R 4 | R 5 | (R 6 ) | R 7 | R 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| alizarin |  |
−OH | −OH | −H | −H | −H | (−H) | −H | −H |
| Alizarin R | −OH | −OH | −OH | −H | −H | (−H) | −H | −H | |
| Alizarin Bordeaux | −OH | −OH | −H | −H | −OH | (−H) | −H | −OH | |
| Purpurin | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | −H | (−H) | −H | −H | |
| Alizarin orange | −OH | −OH | −NO 2 | −H | −H | (−H) | −H | −H | |
| Alizarin red | −OH | −OH | −SO 3 H | −H | −H | (−H) | −H | −H |
use
Alizarin dyes are mainly used to dye wool. As stain dyes, they only adhere to the fibers if they have been previously treated with stains based on metal salts such as. B. aluminum or chromium salts were treated. The corresponding poorly soluble metal complexes ( colored lacquers ) then form on the fiber . The colors are characterized by high color fastness .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Milestone in the pharmaceutical industry: The Bayer factory in Elberfeld until 1923. Accessed December 15, 2018 .
- ↑ Entry on alizarin dyes. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 15, 2018.