Alogliptin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
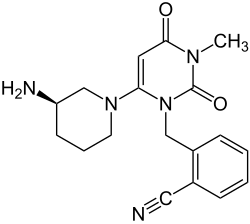
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Alogliptin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
2 - ({6 - [(3 R ) -3-Amino-1-piperidinyl] -3-methyl-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1 (2 H ) -pyrimidinyl} methyl) benzonitrile |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 21 N 5 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 339.39 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Alogliptin is an antidiabetic drug from the group of gliptins for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus .
properties
Alogliptin inhibits dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) and thus promotes the anti-diabetic effects of incretins . The therapeutic efficacy of alogliptin corresponds to that of other inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase 4. In April 2016, the Food and Drug Administration warned of an increased risk of heart failure after taking alogliptin or saxagliptin . Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors can cause joint pain . Alogliptin trade names are Nesine and Vipidia . Combination preparations are Kazano and Vipdomet (both with metformin ) and Oseni and Incresync (with pioglitazone ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Y. Saisho: Alogliptin benzoate for management of type 2 diabetes. In: Vascular health and risk management. Volume 11, 2015, pp. 229–243, doi : 10.2147 / VHRM.S68564 , PMID 25914541 , PMC 4401208 (free full text).
- ^ AB Marino, SW Cole: Alogliptin: safety, efficacy, and clinical implications. In: Journal of pharmacy practice. Volume 28, Number 1, February 2015, pp. 99-106, doi : 10.1177 / 0897190014522063 , PMID 24532820 .
- ↑ FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA adds warnings about heart failure risk to labels of type 2 diabetes medicines containing saxagliptin and alogliptin. In: fda.gov. February 11, 2014, accessed February 12, 2019 .
- ^ AJ Scheen: Cardiovascular Effects of New Oral Glucose-Lowering Agents: DPP-4 and SGLT-2 Inhibitors. In: Circulation research. Volume 122, number 10, May 2018, pp. 1439-1459, doi : 10.1161 / CIRCRESAHA.117.311588 , PMID 29748368 , PMC 5959222 (free full text).
- ↑ FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns that DPP-4 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes may cause severe joint pain. In: fda.gov. October 16, 2006, accessed February 12, 2019 .
- ↑ a b G. M. Keating: Alogliptin: a review of its use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In: Drugs. Volume 75, Number 7, May 2015, pp. 777-796, doi : 10.1007 / s40265-015-0385-y , PMID 25855222 .