Alpha Latrotoxin
| Alpha Latrotoxin | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mass / length primary structure | 1381 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homotetramer | |
| Identifier | ||
| External IDs | ||
| Transporter classification | ||
| TCDB | 1.C.63 | |
| designation | Latrotoxins | |
Alpha-Latrotoxin (α-LTX) is a neurotoxin and the main component of the poison mixture produced in the venomous glands by spiders of the genus Real Widows ( Latrodectus ) .
Mode of action
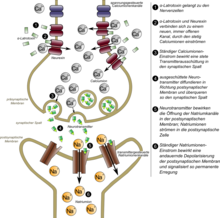
Alpha-latrotoxin is a relatively large-molecule protein that acts on the peripheral nervous system . It acts as a toxin by opening additional calcium channels in the presynaptic nerve cell , in the structure of which the toxin itself probably plays a decisive role and which are particularly permeable to calcium ions (Ca 2+ ). The influx of calcium ions into the cell continuously releases neurotransmitters ( exocytosis ), which results in a permanent nervous signal in the form of high action potential frequencies . Cramps develop. The poison leads to death if the spasms attack the respiratory system and lead to suffocation (due to respiratory failure or due to edema ).
literature
- EV Grishin: Black widow spider toxins: the present and the future. In: Toxicon. 36 (11), November 1998, pp. 1693-1701. doi: 10.1016 / S0041-0101 (98) 00162-7 . PMID 9792186 .
- TC Südhof: alpha-latrotoxin and its receptors: neurexins and CIRL / latrophilins. In: Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 2001, pp. 933-962. doi: 10.1146 / annurev.neuro.24.1.933 . PMID 11520923 .
- YA Ushkaryov, KE Volynski, AC Ashton: The multiple actions of black widow spider toxins and their selective use in neurosecretion studies. In: Toxicon. 43 (5), April 2004, pp. 527-542. doi: 10.1016 / j.toxicon.2004.02.008 . PMID 15066411 .
- YA Ushkaryov, A. Rohou, S. Sugita: α-Latrotoxin and its receptors ". Handbook of experimental pharmacology. In: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 184 (184), 2008, pp. 171-206. Doi : 10.1007 / 978- 3-540-74805-2_7 , ISBN 978-3-540-74804-5 . PMC 2519134 (free full text). PMID 18064415 .
- AW Henkel, Sethuraman Sankaranarayanan: Mechanisms of alpha-latrotoxin action. In: Cell and tissue research. 296 (2), May 1999, pp. 229-233. doi: 10.1007 / s004410051284 . PMID 10382267 .
- ME Peterson: Black widow spider envenomation. In: Clinical techniques in small animal practice. 21 (4), November 2006, pp. 187-190. doi: 10.1053 / j.ctsap.2006.10.003 . PMID 17265903 .
- H. Hiramatsu, S. Tadokoro, M. Nakanishi, N. Hirashima: Latrotoxin-induced exocytosis in mast cells transfected with latrophilin. In: Toxicon. 56 (8), December 2010, pp. 1372-1380. doi: 10.1016 / j.toxicon.2010.08.002 . PMID 20708026 .
- GA Jelinek: Widow spider envenomation (latrodectism): a worldwide problem. In: Wilderness & environmental medicine. 8 (4), November 1997, pp. 226-231. doi : 10.1580 / 1080-6032 (1997) 008 [0226: WSELAW] 2.3.CO; 2 . PMID 11990169 .
- A. Rohou, J. Nield, YA Ushkaryov: Insecticidal toxins from black widow spider venom. In: Toxicon. 49 (4), March 2007, pp. 531-549. doi: 10.1016 / j.toxicon.2006.11.021 . PMC 2517654 (free full text). PMID 17210168 .
- S. Gasparini, N. Kiyatkin, P. Drevet et al .: The low molecular weight protein which co-purifies with alpha-latrotoxin is structurally related to crustacean hyperglycemic hormones. In: J. Biol. Chem. 269 (31), August 1994, pp. 19803-19809. PMID 8051061 .
- Andis Graudins, Michelle J. Little, Sandy S. Pineda, Peter G. Hains, Glenn F. King, Kevin W. Broady, Graham M. Nicholson: Cloning and Activity of a Novel α-latrotoxin from Red-back Spider Venom. In: Biochemical Pharmacology. 83 (1), 1 January 2012, pp. 170-183. doi: 10.1016 / j.bcp.2011.09.024 . PMID 22001442 .
- Rüdiger Wehner, Walter Gering: Zoology . 24th edition. Georg Thieme Verlag KG, Stuttgart 2007, ISBN 978-3-13-367424-9 , p. 404 .