Amino acid fermentation
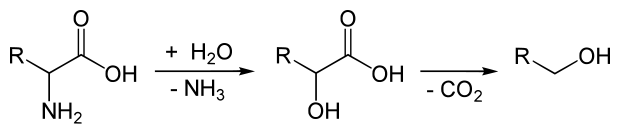
Under amino acid fermentation ( Felix Ehrlich , 1905), in the English language and Ehrlich pathway called, refers to the breakdown of amino acids by yeasts to alcohols . The yeasts or enzymes used in alcoholic fermentation not only ferment the sugar, but also other organic substances such as the amino acids, the breakdown products of which form part of the fusel oils . As a general pattern, Ehrlich gives a deamination with subsequent decarboxylation for the breakdown of amino acids :
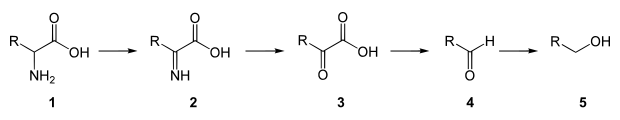
According to Neubauer and Frommherz (1911), amino acid 1 is broken down with the formation of the intermediate products imino acid 2 , keto acid 3 and aldehyde 4 to give alcohol 5 . Except for the last step, like the metabolism in higher organisms, which oxidize the aldehyde to fatty or carboxylic acid R – COOH:
- Amino acid → imino acid → keto acid → aldehyde → alcohol
The following are formed:
- Leucine → optically inactive isoamyl alcohol ( 3-methyl-1-butanol )
- Isoleucine → optically active amyl alcohol ( 2-methylbutyl alcohol )
- Valine → isobutanol ( 2-methyl-1-propanol )
- Glutamic acid → 4-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Tyrosine → 2- (4-hydroxyphenyl) ethanol (tyrosol)
- Tryptophan → indole ethyl alcohol (indole-3-ethanol, tryptophol )
- Histidine → imidazole ethyl alcohol (imidazolyl-4-ethanol, histaminol)
Individual evidence
- ^ EJ Pires, JA Teixeira, T. Brányik, AA Vicente: Yeast: the soul of beer's aroma - a review of flavor-active esters and higher alcohols produced by the brewing yeast. In: Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology . Volume 98, Number 5, March 2014, pp. 1937-1949, ISSN 1432-0614 . doi : 10.1007 / s00253-013-5470-0 . PMID 24384752 .
- ↑ DC Parente, EE Vidal, FC Leite, W. de Barros Pita, MA de Morais: Production of sensory compounds by means of the yeast Dekkera bruxellensis in different nitrogen sources with the prospect of producing cachaça. In: Yeast (Chichester, England). [electronic publication before printing] October 2014, ISSN 1097-0061 . doi : 10.1002 / yea.3051 . PMID 25345668 .