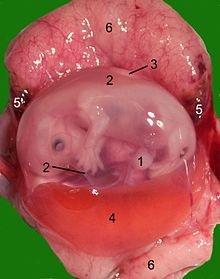
Amnion

Translation of the inscription:
Yolk-sac = yolk sac
Neural groove = neural groove
Primitive streak = primitive streak
Neurenteric canal = neurenteric canal
body stalk = stalk
The amnion ( ancient Greek ἀμνίον amníon , German 'that belongs to the lamb' ), also called sheep skin , is the thin, transparent, vascularless inner egg skin and thus part of the amniotic sac containing the fetus in amniotes such as reptiles, birds and mammals. With them, the chorion ( villi skin ) forms the middle and the decidua (sieve skin) the outer membrane.
The cavity enclosed by the amnion, the amnion cavity , enlarges very quickly during the embryonic development and surrounds the human embryo with its umbilical cord on all sides as early as the fourth week of pregnancy . The fruit side, single-layer epithelial amnion secretes amniotic fluid as amniotic fluid into the amniotic sac. To win it for an examination requires an amniocentesis .
Diseases
- Amniotic ligament syndrome : rupture of the amnion with the formation of fibrous ligaments that constrict the limbs of the unborn child during pregnancy and can then lead to malformations ( dysmelia ).
- Oligohydramnios : There is too little amniotic fluid, which can lead to dysmelia .
- Polyhydramnios : there is too much amniotic fluid.
Others
Amniotic membranes are transplanted to treat surface defects in the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye.
See also
- Amniocentesis (amniotic fluid puncture for prenatal diagnosis)
- Amniotomy (ruptured skin)
- Allantois
literature
- Monika Kressin, Bertram Schnorr: Embryology of Pets. 5th edition. Enke-Verlag, Stuttgart 2006, ISBN 3-8304-1061-1 .