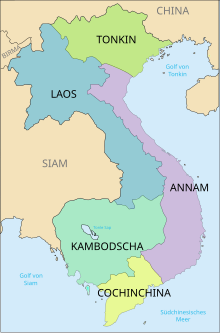
Annam
Annam (Vietnamese An Nam , from Chinese安南, "pacified south") is the historical name for a region in Southeast Asia that extends over the central part of today's Vietnam , between the historical regions of Cochinchina in the south and Tonkin north of the Ma River. From 1834 the region was known in Vietnamese as Trung Kỳ (from Chinese中 圻, "middle border"). In 1884 the French turned the region into a protectorate under the name Kaiserreich Annam (Vietnamese Đế quốc An Nam )
Geography and population
Annam is bordered by Cambodia and Laos to the west and by the South China Sea to the east. The most important city and historical capital is Huế , other important cities are Đà Nẵng and Vinh .
The sparsely populated mountain region in the hinterland of central and southern Vietnam is known as Truong Son or Annamite Highlands . This largest of the five main landscapes of Vietnam is mainly settlement area of ethnic minorities . It is traversed by the Annamite Cordillera (vietn. Dãy Trường Sơn), a 1,100 km long mountain range that also extends to the national territory of Laos . The mountain range runs parallel to the coast of the South China Sea and separates the great plain of the Mekong in the south (see Mekong Delta ) from the narrow, long coastal strip of Central Vietnam. In its northern part is the 2711 m high Phu Xai Lai Leng mountain range . The 56th Statistical Yearbook of France for the period 1940–1945 gives an area of 147,600 m² for Annam (Vietnam a total of 328,000 km²).
The population in 1936 was 5,656,000 (up from 18,972,000 for Vietnam as a whole).
history


In documents from the year 1164 of the Chinese Sung dynasty , the name Annam ( An-nam Quoc ) for the Vietnamese feudal state appeared for the first time.
In 1882 there was armed conflict between China and France over the Annam (and Tonking ) region . With the Peace of Tientsin in 1885, the Chinese finally left Annam to the French as a protectorate . From this time on, Annam only refers to the Trung Bộ region , i.e. Central Vietnam. From then on, the official language was French.
After the end of the Second World War , Annam / Vietnam briefly achieved political independence. But it was only as a result of the resolutions of the Indochina Conference in 1954 that the French withdrew from Annam and from all of Vietnam. The region became part of the Vietnamese state.
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Meyer's New Lexicon in eight volumes. VEB Bibliographisches Institut Leipzig, 1964/65. Volume 1, p. 275.
- ↑ trips to Vietnam; View of the former government palace in Hue , accessed October 31, 2018.
- ↑ Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques: Annuaire Statistique, Cinquante-sixième volume. 1940-45, p. 321.
- ↑ Julius Hirschberg: Um die Erde - A travel description (PDF), accessed on October 31, 2018.