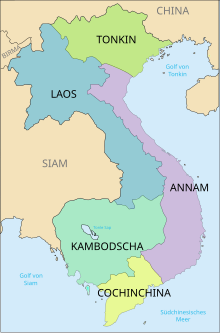
Tonkin

As Tonkin , also Tonkin , Vietnamese Bắc Kỳ (of Chinese北圻, northern border), the northernmost part of was during the French colonial Vietnam , respectively. The term was never officially used by Vietnam. Đông Kinh (東京, eastern capital) was in the Lê dynasty around 1430 the name for what is now called Hanoi . When the Dutch East India Company (VOC) established a trading post here in the 17th century, the name Tonkin found its way into European literature.
geography
Tonkin is bordered to the north by the Chinese Autonomous Region of Guangxi and Yunnan Province , to the west by Laos , to the south by Annam , the central part of Vietnam, and to the east by the Gulf of Tonkin , which is part of the South China Sea . The river Ma forms the border with Annam.
The Tonkin is essentially formed by the lower reaches and delta of the Red River . The fertile plain is primarily used for growing rice . The region is rich in natural resources such as B. Coal and ore .
Important cities in Tonkin are the Vietnamese capital Hanoi and the port city of Hải Phong . Tonkin comprises the three northernmost regions of Vietnam, with these two cities and 23 provinces. The total area covers 114,690 km² and 27,941,700 inhabitants.
The 56th Statistical Yearbook of France for the period 1940–45 gives an area of 115,700 km² (Vietnam a total of 328,000 km²). The population in 1936 was 8.7 million (up from 18,972,000 for Vietnam as a whole).
Off the coast of Tonkin lies Halong Bay , one of the most famous sights of the region and world natural heritage of UNESCO .
history
The course of the Vietnamese-Chinese border was controversial for a long time. Historically, it went back to the Treaty of Tianjin in 1858 (with amendments in 1896), in which the then Chinese Empire had to renounce the Tonkin protectorate and recognize it as a French protectorate . The controversial border line was discussed several times in negotiations between China and Vietnam (including 1957). From the beginning of the 1970s, however, there were frequent border incidents for which both states blamed each other. These border disputes were ultimately one of the reasons for the Sino-Vietnamese War in 1979. It was not until 1999 that the border was contractually established.
The Pentagon Papers , which were compulsorily published in 1971, informed the world public that the United States was deliberately misrepresenting its entry into the Vietnam War with the so-called Tonkin incident .
See also
literature
- Rudolf Schlegel: Tongking . Scientific supplement to the XI. Annual report of the Königlichen Realgymnasium zu Borna, Borna 1913 ( digitized version ).
- Pierre Gourou: Le Tonkin. L'Imprimerie Protat à Macon, Paris 1931.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques: Annuaire Statistique, Cinquante-sixième volume. - 1940-45. Page 321
Coordinates: 21 ° 0 ′ N , 106 ° 0 ′ E