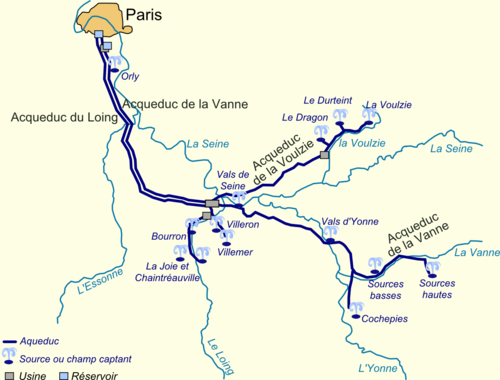
Aqueduc de la Vanne

The Aqueduc de la Vanne is around 156 km long water pipeline from the Yonne department in the region of Bourgogne Franche-Comté to Paris .
The Aqueduc de la Vanne, laid out in the years 1866 to 1874 (after the Aqueduc de la Dhuis ), was the second line to improve the water supply of Paris, which Eugène Belgrand at the instigation of Georges-Eugène Haussmann as part of the Napoléon III. desired urban renewal.
description
The aqueduct is named after the river Vanne , where it starts. It begins in the area of the village of Flacy ( ), where in the gently undulating landscape by the Vanne various springs were found, the Sources Hautes ( High Sources ) are called to distinguish them from the Sources Basses ( Low Sources ) a few kilometers downstream. The line was later extended by the Aqueduc d'Armentiéres ( ) by around 4 kilometers to the east.
![]()
![]()
The water line generally runs underground as a gravity line in pipes between 1.80 m and 2.10 m in diameter. Depressions in the terrain and roads are crossed by a total of 21.5 km of culverts . The culverts are mostly marked by inlet towers that are connected to the terrain by a row of arches. Large bridges cross the Yonne near Villeperrot ( ), the Loing near Moret-sur-Loing ( ), cross the forest of Fontainebleau ( and ) and finally the valley of the Bievre with the Pont-aqueduc d'Arcueil ( ).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The line ended in the Réservoir de Montsouris in Paris ( ), but since 1969 in the newly created Réservoir de l'Haÿ-les-Roses (Val-de-Marne) ( ).
![]()
![]()
After the death of Eugène Belgrand, the Aqueduc de la Vanne was supplemented by the Aqueduc du Loing, built between 1897 and 1900, which in turn was expanded by the two Aqueducs de la Voulzie and du Lunain, built in the 20th century.
The pipe has an average gradient of 13 cm / km, which is enough to let the water flow by gravity alone. The maximum flow rate is 145,000 m³ / day.
The locally available materials were used for the construction. The above-ground structures are therefore mostly made of quarry stone masonry , legally the two bridges in Villeperrot and Moret-sur-Loing are made of rammed concrete and are among the first bridges of this type. The Pont-Aqueduc d'Arcueil near Paris was made of quarry stone masonry on the arches of the Aqueduc Médicis established.
The Aqueduc de la Vanne is operated by Eau de Paris , the Parisian waterworks.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Unlike in German, the term aqueduc in French refers to the entire water supply system including the gravity pipeline , the water-bearing bridge ( le pont-aqueduc ) as well as the penstock and the culvert ( le siphon )
- ↑ Aqueducs des chemins pour l'eau on eaudepari.fr
- ↑ Emploi de béton aggloméré (system Coignet ) in the construction de l'aqueduc de la Vanne . In: Annales des ponts et chaussées. Mémoires et documents relatifs à l'art des constructions et au service de l'ingénieur . 1870, p. 402-405 ( digitized on Gallica ).