Mirach
|
Star Mirach (β Andromedae) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 404, "The Ghost of Mirach" .jpg | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Mirach and the outshone galaxy NGC 404 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| AladinLite | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Observation dates equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Constellation | Andromeda | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Right ascension | 01 h 09 m 43.9 s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| declination | + 35 ° 37 ′ 14 ″ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Apparent brightness | 2.07 mag | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Typing | |||||||||||||||||||||
| B − V color index | +1.58 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| U − B color index | +1.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| R − I index | +1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral class | M0 III | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Astrometry | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Radial velocity | (+0.1 ± 0.2) km / s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| parallax | (16.52 ± 0.56) mas | ||||||||||||||||||||
| distance | (197 ± 7) ly (60.5 ± 2.1) pc |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual absolute brightness M vis | −1.8 mag | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Proper movement | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Rec. Share: | (+175.90 ± 0.60) mas / a | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Dec. portion: | (−112.20 ± 0.46) mas / a | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other names and catalog entries |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Mirach (derived from Arabic via mirat مئزر, DMG miʾzar 'apron') is the name of the star β Andromedae (Beta Andromedae ). Mirach has an apparent magnitude of +2.1 mag and is about 200 light years away (Hipparcos database). Mirach is a red giant of the M0 III spectral type with a surface temperature of around 3300 Kelvin .
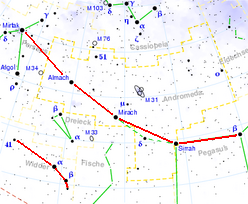
Mirach not only forms the center of the constellation Andromeda , but also the striking five-star row that can be seen in the starry sky of the northern hemisphere almost all year round.
From Mirach 7–8 ° to the northwest stands the well-known Andromeda Nebula (M31), the large neighboring galaxy of our Milky Way, which is mostly visible to the naked eye. With " Starhopping " you can easily find it via the two stars on the right above Mirach.
Furthermore, Mirach is also pretty much in the middle if you draw a line from Andromeda to the Triangle Nebula (M33). In addition, Mirach outshines the galaxy NGC 404 .
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Hipparcos catalog (ESA 1997)
- ↑ a b c Bright Star Catalog
- ↑ Pulkovo radial velocities for 35493 HIP stars
- ↑ a b c Hipparcos, the New Reduction (van Leeuwen, 2007)
- ↑ estimated based on the apparent brightness and distance
