Block vortex
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| M43.2 | Other vertebral fusion |
| Q76.4 | Other congenital malformations of the spine without scoliosis |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The partial or complete fusion of two or more vertebral bodies is referred to as a block vortex . The amalgamation can be caused by a developmental disorder ( dysontogenic block vertebra) or acquired in the course of life.
A dysontogenetic block vertebra formation can be found, for example, in the Klippel-Feil syndrome .
Acquired block vortices can z. B. after inflammation of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs (e.g. after tuberculosis ), after trauma or with pronounced degeneration of the intervertebral discs and adjacent vertebrae ( osteochondrosis intervertebralis ).
Other vertebral abnormalities
- Numerical segmentation anomalies (e.g. 6 instead of 5 lumbar vertebrae) - transition vertebrae
- Surplus ribs ( cervical rib , lumbar rib )
- Half vortex
- Split vertebrae
- Arc closure anomalies
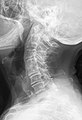
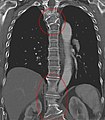
Several congenital block vertebrae in the transition from the thoracic to the lumbar spine and hemi-vertebrae with hemimetameric segment shift in the upper thoracic spine.
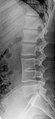
Congenital block vertebrae in the lumbar spine (partially LWK 3 and 4). The back part of the intervertebral disc is still preserved.
literature
- Rüdiger Döhler , Holger von Kroge, Friedrich Hennig : Clinical significance of cervical block vertebrae . chirurgische praxis 52 (1997), pp. 317-324.
- Koehler, Zimmer: Limits of the normal and the beginnings of the pathological in the X-ray image of the skeleton . Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart, New York, 1989, ISBN 3-13-111723-0
- Wolfgang Dihlmann : Joints - vertebral connections . Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart, New York, 2002 ISBN 3-13-132013-3
- Klippel-Feil Syndrome. In: Netters general medicine. Edited by Thomas Böttcher and Martin Kortenhaus. Stuttgart 2006 ISBN 3-13-135881-5 p. 840
Web links
- Information on congenital scoliosis at skoliosen.de