Bremelanotide
| Bremelanotide | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
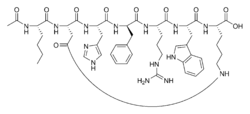
| Structural formula | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 7 amino acids (cyclic), 1025 daltons | |
| Identifier | ||
| External IDs |
|
|
Bremelanotide is a drug selected from the group of the melanocortin - agonists . It was approved in the United States in June 2019 under the trade name Vyleesi (marketing authorization holder: AMAG Pharmaceuticals ) for the treatment of so-called hypoactive sexual regulation disorder in women before menopause .
development
Initially intended to increase the tanning ability of self-tanning creams , unexpected effects such as increased sexual desire and the occurrence of erections have been observed in tests . In contrast to PDE-5 inhibitors such. B. Sildenafil ( Viagra ) does not work Bremelanotide by promoting blood flow, but by stimulating sexual desire in the brain ( aphrodisiac effect).
The company Palatin Technologies first tested a nasal spray with the active ingredient. However, development was discontinued after Phase II clinical trials due to side effects (increased blood pressure, nausea and vomiting). Experiments followed with a formulation to be used subcutaneously with the aim of reducing the side effects.
In 2019, the drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration under the name Vyleesi . The product distributed by AMAG Pharmaceuticals will be sold in the USA from September 2019. It is not approved for the EU. The agent is injected subcutaneously .
Chemical structure
Bremelanotide is a cyclic heptapeptide - lactam with the primary structure Ac-Nle- cyclo [Asp-His- D -Phe-Arg-Trp-Lys] -OH and a metabolite of Melanotan II . Bremelanotide differs from Melanotan II only in that it has a C-terminal hydroxyl group instead of the amide group .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Office of the Commissioner: FDA approves new treatment for hypoactive sexual desire disorder in premenopausal women. June 21, 2019, accessed June 24, 2019 .
- ^ A b Mac E. Hadley, Robert T. Dorr: Melanocortin peptide therapeutics: historical milestones, clinical studies and commercialization. In: Peptides . Vol. 27, No. 4, 2006, pp. 921-930, PMID 16412534 , doi : 10.1016 / j.peptides.2005.01.029 .
- ↑ a b Palatin Technologies: Bremelanotide for Female Sexual Dysfunction . ( Memento from January 26, 2016 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ US National Institutes of Health: 4 studies found for: Bremelanotide. On clinicaltrials.gov ; last accessed on January 21, 2016.
- ↑ FDA allows bremelanotide for sexual hypofunction on deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de
- ↑ New drug for more pleasure in women on pharmische-zeitung.de
Web links
- Information of the license holder (English)
- SPON from June 24, 2019: "Vyleesi" pleasure drug approved for women - share price rises
