Calmodulin
| Calmodulin | ||
|---|---|---|
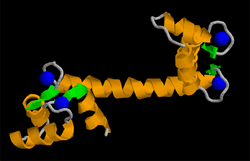
|
||
| according to PDB 1CLL . Ca 2+ : blue, alpha-helices: orange, beta-sheets: green | ||
|
Existing structural data: s. UniProt |
||
| Mass / length primary structure | 148 amino acids | |
| Cofactor | 4 calcium | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name (s) | CALM1 , CALM2 , CALM3 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Calmodulin | |
| Parent taxon | Chordates | |
Calmodulin ( CaM ) is a calcium- binding regulatory protein that is highly conserved in all eukaryotes . Calmodulin plays an important role as a second messenger because it is not enzymatically active itself, but is responsible for activating other proteins. It belongs to the group of EF hand proteins. The structure of the calcium-binding region, which forms a typical helix-loop-helix structure, is called the EF hand . This family of proteins to which u. a. Troponin C , parvalbumin and calbindin , is one of the two important calcium-binding protein families, plus the group of annexins . Calmodulin in humans in the smooth muscle of actin bound to find where it is the contraction regulated.
Three alleles are known which code for the identical protein.
The targets of the active Ca 2+ / calmodulin complex are, for example, CaM-dependent kinase (CaMK), adenylyl cyclase , myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) , phosphatase calcineurin and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS).
Some substances such as W-7 act as calmodulin inhibitors by transporting the calcium out of the cell, which is necessary for enzyme activation.
Web links
- Jennifer McDowall / Interpro: Protein Of The Month: Calmodulin. (engl.)
- SVU / Proteopedia: Calmodulin in motion
- SVU / vimeo: Calmodulin (molecular dynamics as video)