Campbell Glacier
| Campbell Glacier | ||
|---|---|---|
|
The Cambell Glacier (at the top) north of the Terra Nova Bay bounded by the Drygalski ice tongue in the south |
||
| location | Victoria Land , East Antarctica | |
| length | 100 km (rough estimate) | |
| Coordinates | 74 ° 25 ′ S , 164 ° 22 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| drainage | Terra Nova Bay , Ross Sea | |
|
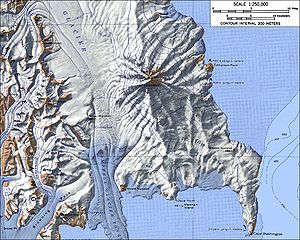
Topographic map of the Campbell Glacier and its tongue between the Deep Freeze Range (left) and Mount Melbourne (right) |
||
The Campbell Glacier is a 100 km long glacier in East Antarctica, Victoria Land . It flows from the south end of the Mesa Range in a south-easterly direction between the Deep Freeze Range and Mount Melbourne and flows into the Scott coast in the form of the Campbell glacier tongue ( 74 ° 36 ′ 0 ″ S , 164 ° 42 ′ 0 ″ E ) northern section of Terra Nova Bay .
The lower section of the glacier was discovered by the northern group of the Terra Nova Expedition (1910-1913) led by British polar explorer Victor Campbell (1875-1956) . US and New Zealand land surveys recorded the geographic extent of the glacier area between 1961 and 1964. This led to the refutation of Campbell's erroneous assumption that the glacier flows into the Nansen ice table instead of into Terra Nova Bay .
Web links
- Campbell Glacier in the Geographic Names Information System of the United States Geological Survey (English)
- Campbell Glacier on geographic.org (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Campbell Glacier Tongue on geographic.org (accessed November 10, 2015).