Chyme

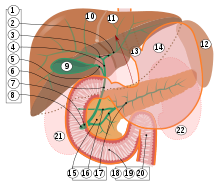
Chyme ( ancient Greek χυμός chymos , German , juice ' ) is the chyme that in the stomach under the action of digestive secretions ( saliva and digestive enzyme - and hydrochloric acid -rich gastric juice ) is produced from the recorded food. This process is known as chymification . The chyme is mixed by the stomach contraction and then released in portions to the duodenum , the first section of the small intestine , via the stomach gate ( pylorus ) . The chyme is acidic, with an average pH value of around 2. To increase the pH value when entering the duodenum and alkalize the chyme , the gall bladder is contracted under the influence of the hormone cholecystokinin (CCK) , which causes bile is released into the duodenum with plenty of sodium hydrogen carbonate and the chyme is largely neutralized there before it reaches the jejunum , the second section of the small intestine.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Online Etymology Dictionary: chyme ( English ). Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- ^ Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott: A Greek-English Lexicon, Perseus Digital Library: χυμός ( English ) Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- ↑ Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary: chyme . Retrieved March 2, 2013.