Cirrhinus molitorella
| Cirrhinus molitorella | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
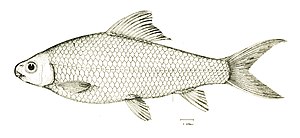
Cirrhinus molitorella |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Cirrhinus molitorella | ||||||||||||
| ( Valenciennes , 1844) |
Cirrhinus molitorella (English Mud Carp) is a medium-sized carp fish from Indochina and southern China. He is also called White Lady Carp, in Cambodia Trey Kawlang, Pa Geng in Laos, Cape Lumpur in Malaysia, 侧 斑 鲮 in China and in Vietnam CáTrôi Việt.
description
It has 37 to 43 scales on its lateral line and thus differs from Cirrhinus microlepis . Its fin formula is: Dorsal 11–15. Another distinguishing feature are the color drawings on its scales, which are particularly evident in freshly caught specimens. The colors vary from blue-green to blue-black. The fish are usually 15 to 50 centimeters long. In the Chinese Guangdong Province, an approximately 100 cm long and 11.25 heavy specimen was caught with a fishing rod.
distribution
The distribution area of Cirrhinus molitorella extends from the river basins of the Mae Nam Chao Phraya , Nam Theun, Xe Bangfai, Mekong and Nanpangjiang , Pearl River to the Red River in China and Vietnam. Thus, they occur in the People's Republic of China , Vietnam , Laos , Cambodia and Thailand . Also in Hong Kong , Malaysia , Indonesia and Singapore . The fish species was introduced to Taiwan and Panama .
Way of life
Cirrhinus molitorella lives in tropical waters such as medium-sized to large rivers and streams with temperatures of 22 to 26 ° C, where it is mainly in the mean water to near the ground at depths of about five to 20 meters. Water temperatures below 7 ° C are not tolerated. During the rainy season, it migrates to the flooded forests and feeds on algae , phytoplankton and detritus . He is considered omnivorous . Like its relative, Cirrhinus microlepis , Cirrhinus molitorella also prefers the areas around rapids and deeper backwater zones. Wild animals show pronounced migratory behavior, while domesticated strains of Cirrhinus molitorella largely abandon this behavior. They depend on running water and cannot be kept for long in ponds where they cannot reproduce. They reach sexual maturity around the age of three.
Use
Cirrhinus molitorella is an important food fish locally and has a high nutritional value. Larger specimens are freshly marketed and smaller ones processed into prahok . In the Chinese Pearl River , Cirrhinus molitorella has been cultivated for a long time, and today it is of the greatest economic importance in China of all Asian countries. There they are mainly kept in polyculture with other food fish.
literature
- Cai Renkui: Development History of Freshwater Culture in China . China Press of Science & Technology, Beijing 1991.
- Wu Xianwen: Ichthyography of Cyprinidae in China (Upper Volume). Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai 1964.
Web links
- [1] FAO report on Cirrhinus molitorella
- [2] Reproduction and nursing of Cirrhinus molitorella in a small fish farm in Luang Prabang Province, Lao PDR
- SH Bowen, B. Gu and Zhanghan Huang: Diet and Digestion in Chinese Mud Carp Cirrhinus molitorella Compared with Other Ilyophagous Fishes on [3]
- [4] Production of Cirrhinus molitorella and Labeo chrysophekadion for culture based fisheries development in Lao
- Cirrhinus molitorella inthe IUCN 2013 Red List of Threatened Species . Posted by: Nguyen, THT, Van, NS & Thinh, DV, 2010. Retrieved December 17, 2013.
Notes and individual references
- ↑ Transl. Mud carp
- ↑ a b c d e Cirrhinus molitorella on Fishbase.org (English)
- ^ Fishing World Records
- ↑ a b c d e http://www.fao.org/fishery/culturedspecies/Cirrhinus_molitorella/en
- ↑ Laotian fish spice on http://www.asianonlinerecipe.com/food-glossary/prahoc.php