Coenzyme A Synthase
| Coenzyme A Synthase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 564 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | COASY | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme Classifications | ||
| EC, category | 2.7.7.3 , Transferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of an adenylyl residue | |
| Substrate | Phosphopantethein + ATP | |
| Products | Dephospho-Coenzyme A + ADP | |
| EC, category | 2.7.1.24 , kinase | |
| Response type | Phosphorylation | |
| Substrate | Dephospho-coenzyme A + ATP | |
| Products | Coenzyme A + PP i | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Coenzyme A synthetase | |
| Parent taxon | Bilateria | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 80347 | 71743 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000068120 | ENSMUSG00000001755 |
| UniProt | Q13057 | mm10 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_001042529 | XM_006534257 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_001035994 | XP_006534320 |
| Gene locus | Chr 17: 42.56 - 42.57 Mb | Chr 11: 101.08 - 101.09 Mb |
| PubMed search | 80347 |
71743
|
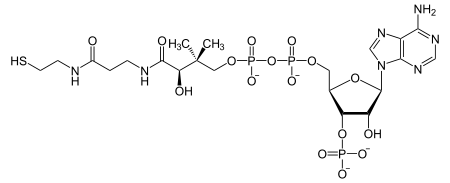
Coenzyme A synthetase is the enzyme that the last two sub-steps in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A catalyzed . This dual function enzyme is found in all animals, while bacteria, fungi and plants have two separate enzymes. In humans CoA synthetase is in all tissue types in the cytosol to the mitochondria - membrane localized, particularly hard it is produced in the liver and kidneys.
Catalyzed reactions
One of two separate domains on the enzyme is responsible for each partial reaction :
First, an adenylyl residue is transferred to 4'-phosphopantethein with the help of the phosphopantethein adenylyl transferase domain ( EC 2.7.7.3 ), resulting in dephospho-coenzyme A.
Then Dephospho-CoA is phosphorylated to CoA using the Dephospho-CoA kinase domain ( EC 2.7.1.24 ).