Compaq Portable 386
| Compaq Portable 386 | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Manufacturer | Compaq Computer Corporation , United States |
| Sales start | 1987 |
| predecessor | Compaq Portable III |
| successor | Compaq Portable 486 |
| Technical specifications | |
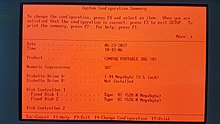
| Mass storage | 40 or 100 MB IDE |
| processor | Intel 80386 @ 20 MHz , Intel 80387 ( FPU ) option |
| random access memory | 1 - 10 MB RAM |
| screen | 10 " amber gas plasma display |
| Current operating system | COMPAQ-DOS 3.31 |
| Connectivity | |
|
connections |
|
| battery pack | |
| Type | None |
| measures and weight | |
| Dimensions (H × W × D) | 248 mm × 410 mm × 192 mm |
| Weight | 11 kg |
The Compaq Portable 386/20 is an IBM-compatible computer in the form of a portable . It was introduced in 1987 by Compaq Computer Corporation .
With a considerable 11 kg weight in the standard version, it is one of the last representatives of the "suitcase computer", but it has built in a very powerful Intel 80386 processor. In contrast to today's portable devices, it does not have a battery and is supplied with power by an AT computer power supply, but internally uses mostly proprietary connections.
Technical data in detail
CPU and FPU
The name giver for this model is the socketed 386DX processor with 20 MHz. The device also provides a socket for a 20 MHz 387 floating point unit , which is not included in the standard equipment.
Since the entire system bus runs at processor speed on 386 computers , an increase in the clock frequency of the processor by replacing it is only possible by using a Cyrix 486DRx2 20/40 , which doubles the clock rate due to a multiplier of 2 (386 pinout-compatible 486 with 1 kB L1 cache), possible.
random access memory
The motherboard itself can hold a total of four 512 kB SIMMs in a proprietary format ( called SC-RAM by Compaq ).
Compaq also provided several expansion cards that can expand the memory up to 10 MB.
- The 32-bit memory / modem carrier board , which is only available as an option , is required to provide the connections for additional RAM cards.
- An expansion card with 4 MB (8 × 512 kB 80 ns, 4 MB memory expansion board) is plugged into this, and
- this, in turn, is required to plug another 4 MB (8 × 512 kB 80 ns, 4 MB additional memory board) card onto it.
The main memory can be expanded to up to 10 MB (2 MB main board, 8 MB with expansion cards).
graphic card
The graphics card can only be set between CGA and MDA emulation using jumpers . The CGA output is, however, required for the Compaq Plasma Display driver from Windows or generally for graphic output. In addition to the CGA standard (640 × 200 pixels), the integrated graphics card can display a maximum resolution of 640 × 400 pixels with two colors (monochrome), but is otherwise fully compatible with the graphics and text standards of the pre- EGA era . The internal display , known as Compaq Portable Plasma , offers a resolution of 640 × 400 pixels with 16 gray levels and is connected directly to the CGA board by means of a proprietary connection.
A better ISA bus graphics card can be retrofitted via the Compaq Expansion Unit , but it cannot be used with the internal display.
hard disk
The device provides two bays for 5.25 " half-height drives , one of which is equipped with a mounting frame for a 3.5" hard drive.
Compaq officially offered two hard drive models with either 40 MB or 100 MB. As was common for devices of this time, only preconfigured type numbers can be specified in the BIOS instead of freely specifying CHS values (for example type 17 with 40 MB or type 42 with 504 MB). In addition, the BIOS is limited to hard drives up to a maximum of 504 MB ( CHS barrier ). A disk manager such as Ez-Drive is therefore necessary for hard drives over 504 MB .
Furthermore, with the IDE connection built in by Compaq , normal 2.5 ″ notebook hard disks or CompactFlash cards (provided they work without LBA ) can also be operated via an adapter . In conjunction with this, the then free 5.25 ″ slot can also be used for a CD-ROM drive, for example .
Floppy disk drive
In its standard version, the device was delivered with a 5.25 ″ 1.2 MB floppy disk drive , but there was the option of installing a second 5.25 ″ 360 kB floppy disk drive instead of a hard disk . A standard ribbon cable is used as in desktop computers, so the installation of a 3.5 ″ 1.44 MB floppy disk drive is not a problem , also thanks to the support provided by the BIOS .
External expansion options
In order to be able to market the device as a professional partner in everyday office life, Compaq also offered external expansion units. However, it is not possible to change the expansion units during operation.
- Compaq Expansion Unit
- As previously mentioned, the device can the (to German expansion unit called) Unit expansion will be expanded. This is a housing attachment with two full-length 16-bit ISA slots . Without exception, all ISA bus cards that have ever appeared can be used in this.
- For example, Compaq marketed a COMPAQ-VG control card which can display text and graphics on an external Compaq VG monitor in - for the circumstances at the time - high resolution (maximum 720 × 400 pixels for text, 640 × 480 pixels for graphics with up to to 256 (from a palette of 256,000) different colors at the same time).
- Compaq Expansion Unit with 40 MB tape drive
- Instead of the ISA slot expansion unit , a 40 MB tape drive from Compaq can also be installed. The case itself looks identical to the normal expansion unit.
Internal expansion cards
Compaq offered various expansion cards, which can be connected via a proprietary connector inside the housing without an expansion unit.
It is not possible to change the expansion cards during operation.
- 32-bit memory / modem carrier board
- The memory expansions, the second asynchronous interface board or modems are connected to the motherboard with the 32-bit memory / modem carrier board (referred to as carrier board in the following).
- 1-2 MB memory expansion board
- 1 MB RAM is already soldered to the 1–2 MB memory expansion board and accepts 1 MB SC-RAM memory modules (2 × 512 kB each) , which are also used on the main board. With this board, the working memory of the portable can be expanded from 2 MB (main board) to 3 or 4 MB. Assumes the carrier board , cannot be used together with one of the following two 4 MB boards .
- 4 MB memory expansion board
- 4 MB RAM are firmly soldered to this circuit board and expands the working memory of the portable to a total of 6 MB. Assumes the carrier board, cannot be used with a 1–2 MB memory expansion board.
- 4MB add-on memory board
- The board is plugged onto an already installed 4 MB memory expansion board , which increases the working memory to a total of 10 MB. Requires the carrier board and 4 MB memory expansion board , cannot be used together with a 1–2 MB board .
- Asynchronous interface board
- This expansion card, known by Compaq as the second asynchronous board (the first board represents an ISA card for the expansion unit ), provides an RS232 connection. Cannot be used at the same time as the carrier board.
- 1200 or 2400 baud modem
- These modems, which were only available as a set, consist of a 1200 or 2400 baud modem compatible with the Hayes command set , a carrier board , a housing cover and a telephone cable for the American and Canadian market. The modem has not been approved for operation in Germany.
BIOS
In contrast to other devices, the BIOS configuration program is not stored directly on a chip, but has to be loaded from a floppy disk. If you no longer have them, you can still find them easily on the Internet today:
- 3.5 ″ - 720 KB version: SP0308.EXE or SP0308.ZIP
- 5.25 ″ 360 KB version: SP0316.EXE or SP0316.ZIP
software
The Compaq Portable was delivered with COMPAQ-DOS version 3.31 as standard. This is fully compatible with MS-DOS 3.2 through reverse engineering , but already offers support for FAT16 hard disks over 32 MB.
Among other things, a User Programs floppy disk was supplied on which programs for memory management and influencing the processor speed (between 6, 8 and 20 MHz) are available. These would be:
- ADAPT.COM (Advanced Display Attribute Programming Tool) is a TSR program to control the character display of the MDA / CGA graphics card using a key combination
- CACHE.EXE (Compaq Disk Cache) serves as a hard disk cache similar to SmartDrive
- CEMM.EXE ( 386 CPU ) / CEMMP.EXE ( 286 CPU ) serves as Expanded Memory Manager, is incompatible with Windows 3.1 (Compaq Expanded Memory Manager)
- CHARSET.COM installs an alternative character set or an alternative font (THINUS) to improve the character representation on the plasma display
- CLOCK.SYS is a driver for the real-time clock of the Portable 386
- MODE.COM replaces MODE.COM supplied by DOS and allows you to switch between graphics modes and processor speeds using commands such as "MODE SEL MDA", "MODE SEL CGA", "MODE SPEED HIGH", "MODE SPEED LOW"
- VDISK.SYS is a RAM drive driver
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ http://mypage.intergate.ca/~fspencer/8580proc.htm
- ↑ COMPAQ Portable 386 Personal Computer USER MANUAL Third edition. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on June 23, 2017 ; accessed on June 23, 2017 .
- ↑ COMPAQ Portable 386 Personal Computer MAINTENANCE AND SERVICE GUIDE. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on June 23, 2017 ; accessed on June 23, 2017 .
- ↑ Compaq Portable Plasma Display under Windows for Workgroups 3.1x. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on July 15, 2015 ; accessed on June 23, 2017 .