Dogtrot House
The dogtrot house or Breezeway House was in the 19th and early 20th centuries a typical construction in the southern states of the USA . It probably originated in the southern Appalachians . The architectural style was mainly developed in Kentucky and Tennessee and used early in the Piedmont . Even today, Dogtrot houses are built from modern building materials according to the historical design.
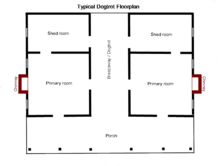
design
The Dogtrot house used to consist of two log houses under one roof with a passage in between (English dogtrot or breezeway ). Usually one log cabin was used for cooking and eating and the other for sleeping. It usually has 1 to 1½ floors and at least two rooms, each 5.5 to 6 m wide, with doors to the centrally located passage. Occasionally, additional rooms or sheds are built on to flank the passage at the front or back. The roofing of the passage provided protection from the heat and natural ventilation of the adjacent rooms.
The chimneys were mostly attached to the two ends of the gable. If there was an upper floor, the stairs were usually in one of the two rooms or in the passage. Some Dogtrot houses only had the open central passage and the flanking rooms, but most had a veranda across the entire width in the front or back.
Preserved buildings
Several Dogtrot houses have been preserved in Dubach , Louisiana , giving the city the state nickname "Dogtrot Capital of the World".
The Dogtrot-style James Jackson Bryan House from 1840 is located on the Azalea Ranch to the south of Webster Parish , Louisiana and formerly belonged to Senator Harold Montgomery . It was inscribed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1999.
The Noel Owen Neal House near Nashville , Arkansas was built in 1840 in the Dogtrot style. It has since been relocated to Washington , Arkansas.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Robert Gamble: Historic architecture in Alabama: a guide to styles and types, 1810-1930 . University of Alabama Press, Tuscaloosa 1990, ISBN 0-8173-1134-3 , pp. 24-29.
- ^ Dog-Run Houses . In: Texas State Historical Association . Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved July 17, 2011.
- ^ A b c Virginia McAlester, Lee McAlester: A Field Guide to American Houses . Alfred A. Knopf, New York 1986, ISBN 0-394-51032-1 , pp. 83-85.
- ^ "Dogtrot House, Poplarville, MS Waggonner & Ball Architects" Architectural Record , By Ingrid Spencer. Retrieved August 11, 2008.
- ↑ "Dogtrot House - Vernacular" , Architecture Week , Great Buildings. Retrieved August 11, 2008.
- ↑ "News Notes: Dogtrot Capital Receives a New Find" , Louisiana Life magazine (November 21, 2006). Retrieved August 11, 2008.
- ^ Town of Dubach, Louisiana Home Page . Retrieved August 11, 2008.
- ↑ Louisiana historical marker, Ranch Azalea, Harold Montgomery Road, Webster Parish, Louisiana
- ↑ 2005 Most Endangered Places . Historic Preservation Alliance of Arkansas.