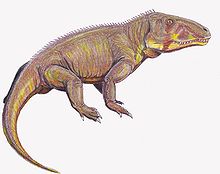
Erythrosuchidae
| Erythrosuchidae | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||
| Temporal occurrence | ||||||||||||
| Lower to middle Triassic | ||||||||||||
| 250 to 232 million years | ||||||||||||
| Locations | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Erythrosuchidae | ||||||||||||
| Broom , 1905 |
The Erythrosuchidae are an extinct group of carnivorous reptiles from the Lower to Middle Triassic . They were large animals 2.5 to 5 meters long with massive bodies. Like the Permian Anteosaurus from the Dinocephalia group and many Temnospondyli , the Erythrosuchidae had particularly large heads, up to a meter long. The heads reached half of the body length in some genera (without the tail). The necks of the animals were massive and short, the cervical vertebrae extremely short to support the great weight. Since the articulation surfaces between the leg bones and those between the leg and carpal bones were only weakly ossified, an aquatic way of life is assumed. In the Lower Triassic, the Erythrosuchidae were the largest terrestrial vertebrates .
They share a number of synapomorphies with later archosaurs that the early archosauromorphs such as the protorosauria lack and are therefore placed in the more anatomically advanced archosauriformes .
Genera
- Chalishevia
- Cuyosuchus
- Dongusia
- Erythrosuchus
- Fugusuchus
- Garjainia
- Shansisuchus
- Uralosaurus
- Vjushkovia
literature
- Michael J. Benton, James M. Clark: Archosaur phylogeny and the relationships of the Crocodylia. In: Michael J. Benton (Ed.): The phylogeny and classification of the Tetrapods. (Proceedings of a Symposium held in London, UK, March 1987). Volume 1: Amphibians, reptiles, birds (= Systematics Association. Special Volume. 35, A). Clarendon Press, Oxford et al. 1988, ISBN 0-19-857705-2 , pp. 295-338, digitized version (PDF; 907.15 kB) .
- Robert L. Carroll : Paleontology and Evolution of the Vertebrates. Thieme, Stuttgart et al. 1993, ISBN 3-13-774401-6 .
- David J. Gover: The tarsus of erythrosuchid archosaurs, and implications for early diapsid phylogeny. In: Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. Vol. 116, No. 4, 1996, ISSN 0024-4082 , pp. 347-375, doi : 10.1111 / j.1096-3642.1996.tb00128.x , digitized version (PDF; 281.18 kB) .
- Martin Sander : Reptiles. 220 individual representations (= Haeckel library. Vol. 3). Enke, Stuttgart 1994, ISBN 3-432-26021-0 .
Web links
- Mikko's Phylogeny Archive Erythrosuchidae
- Palaeos.com